Bytes are the foundation of all digital data, devices, and software, from computer processors to operating systems in everyday electronics. Therefore, training models for next byte prediction can potentially lead to a paradigm shift in deep learning, allowing them to truly understand and simulate all activities in the digital world. This has practical benefits not only in conventional areas, but also in some underexplored areas such as boosting cybersecurity, improving computer diagnostics, optimizing data compression, and even advancing complex tasks like reverse-engineering the source code of that software from its binary representation.
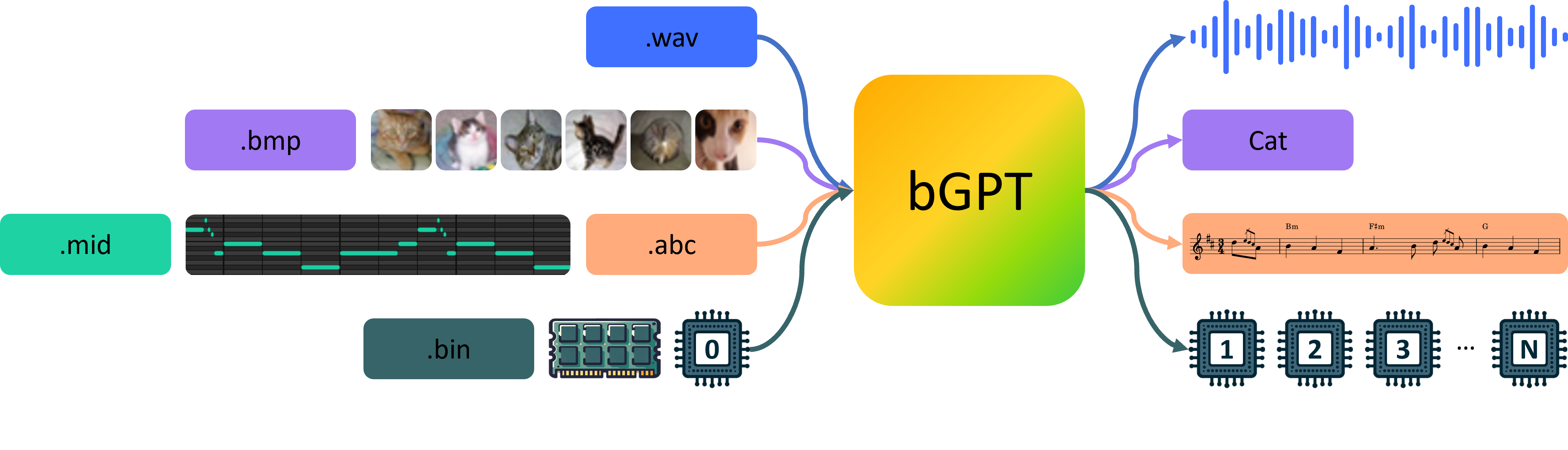
Paper has introduced bGPT, a model designed for binary data processing and digital world modeling by next byte prediction. bGPT segments byte sequences into patches, predicts next patch features with a patch-level decoder, and reconstructs bytes within patches using these features with a byte-level decoder. Its advantages are twofold: 1) Interpreting Digital System: By training on byte sequences, bGPT can learn the patterns of digital systems, enabling it to predict, simulate, and diagnose algorithm or hardware behavior. This ability allows for the reconstruction of complex systems from binary data. 2) Unified Modeling: bGPT integrates various data types into a single framework, treating everything as a byte sequence. This simplifies modeling and allows for easy integration of various data sources.
Experimentation include two main areas: 1) well-studied tasks like generative modeling and classification on digital media data (e.g., text, audio, and images); and 2) relatively underexplored tasks intrinsic to binary-native operations, including data conversion and CPU state modeling, which represent algorithm and hardware simulation, respectively. bGPT models were pre-trained on IrishMAN for data conversion, CPU states for CPU state modeling, Wikipedia for text (achieved a score of 1.0639 BPB and an accuracy of 92.49%), ImageNet for images (achieved a score of 3.12 BPB and an accuracy of 88.69%), and LibriSpeech for audio (achieved a score of 1.48 BPB and an accuracy of 93.63%). All showcased generative samples from bGPT are produced using the same data preprocessing, model architecture, hyperparameters, and training objectives, without any modality-specific customizations.
Paper : https://arxiv.org/abs/2402.19155