Recently, State-of-the-art Transformer-SSM hybrid Architecture has been a driving force in Open source LLMs. Inline with such trends researchers from Zyphra have launched Zamba, a novel 7B SSM-transformer hybrid model which achieves competitive performance against leading open-weight models at a comparable scale. Zamba is trained on 1T tokens from openly available datasets and is the best non-transformer model at this scale.
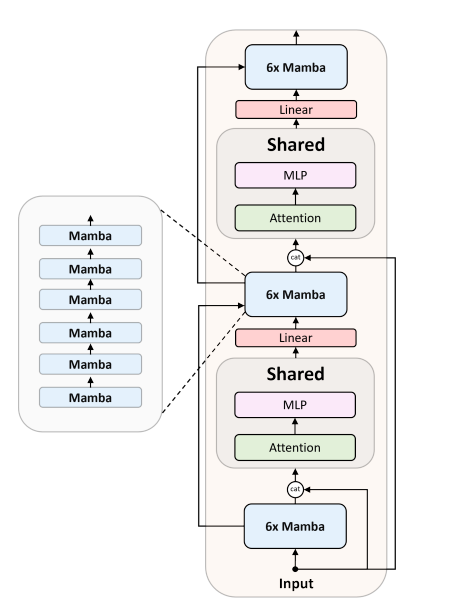
The Zamba architecture consists of a backbone of standard Mamba blocks connected to a shared attention and MLP block. This block is repeated every 6 Mamba blocks but has shared parameters, which enables Mamba to utilize more FLOPs for increased performance at the same memory cost. The input embeddings are always concatenated with the residual stream going into the shared attention block as this provides an additional path for the model to remember the inputs. After the block, a learnt linear projection maps the output back to the residual stream.
Due to its architecture, Zamba is significantly faster at inference than comparable transformer models and requires substantially less memory for generation of long sequences. Zamba is pretrained in two phases: the first phase is based on existing web datasets, while the second one consists of annealing the model over high quality instruct and synthetic datasets, and is characterized by a rapid learning rate decay
Zamba is also the highest-performing SSM in the small 7B model range and the highest-performing dense SSM model available. Zamba matches state-of-the-art 7B models on many linguistic evals, while lagging slightly behind on tests of reasoning and in context learning, which may be due to the significant data disparity between Zamba and other leading ∼7B models.
Paper : https://arxiv.org/pdf/2405.16712