Imagine a personal assistant observing what you do in your daily life. When you ask for recommendations on anything from restaurants and activities to movies, books, and products, based on her in-depth understanding of you she will provide suggestions tailored specifically to your tastes.
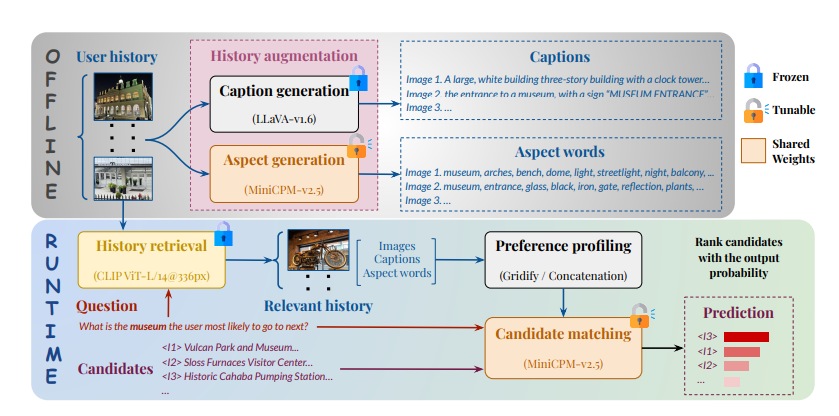
Now researchers from Meta have put this in action with the introduction of VisualLens, a novel approach that extracts, filters, and refines image representations, and leverages these signals for personalization.
At the core of the solution is a set of models that effectively extract the essential signals from the visual history to infer the user’s preferences. First, given a recommendation request, VisualLens selectively retrieves only the most relevant images, thereby reducing unnecessary noises and distractions. Second, to effectively capture the signals a photo may convey, VisualLens uses not only visual embeddings but also text captions and aspect words extracted from the image. Third, VisualLens adopts an iterative refinement process that continually improves aspect extraction to better reflect user interests and inform recommendations. By jointly training aspect word extraction and prediction tasks within a unified model, VisualLens not only reduces the overall parameter size, but also enhances the model’s capability to understand and utilize the visual history for accurate recommendation.
A comprehensive experimental study shows promising recommendation quality of VisualLens. It achieved 82-91% Hit@10 on the Google Review-V and Yelp-V benchmarks, out-performing state-of-the-art UniMP by ∼10%. Even compared with GPT-4o, 8B model outperforms on all metrics, improving Hit@3 by 1.6% and 4.6% respectively on the two benchmarks.