Visual language models (VLMs) have rapidly progressed, driven by the success of large language models (LLMs). However data curation of VLMs still remains under-explored. Given the costly nature of VLM training, most methods are confined with coarse-quality large-scale captioning image-text pairs (pretraining), followed by fine-grained small-scale supervised finetuning (SFT). Recent methods have observed rewarding distillation possibilities from GPT-4V and Gemini. However, the performance is upper bound by these models.
So is it possible that the VLM itself can remedy dataset deficiency and enhance its training ?
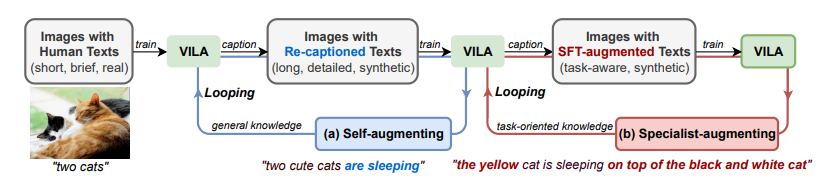
To address this, researchers from Nvidia have introduced VILA-augmented VILA (VILA2), a novel approach that includes a self-augment step and a specialist-augment step to iteratively improve data quality and model performance. VILA2 consists of two main steps: a self-augment step and a specialist augment step.
In the self-augment step, a VLM recaptions its own pre-training data to enhance data quality, and then retrains from scratch using this refined dataset to improve model performance. This process can iterate for several rounds. Once self-augmentation saturates, VILA2 employs several specialist VLMs finetuned from the self-augmented VLM with domain-specific expertise, to further infuse specialist knowledge into the generalist VLM through task-oriented recaptioning and retraining.
In general, VILA2 re-formulate visual language model (VLM) training with a model in the loop to remedy training data defficacy. Then start with validating design options in constructing a self-augmenting loop to improve on caption quality of the default training task. After the saturation of this process, VLM is challenge to generate data conforming to extra SFT-enabled tasks to further VLM learning.
VILA2 based foundational model consistently improves the accuracy on a wide range of tasks over prior art, and achieves new state-of-the-art results on MMMU leaderboard among open-sourced models.
Paper : https://arxiv.org/pdf/2407.17453