Large language models (LLMs) have revolutionized the field of user modeling and personalization due to its ability to learn and adapt from massive amounts of textual data. By analyzing user interactions and understanding user preferences, LLMs can be leveraged to power recommendations, language generation, summarization, and question answering in ways that are highly relevant and engaging to users.
However, user interaction data is often complex, spanning multiple journeys with sparse data points, various interaction types (multimodal), and potential noise or inconsistencies. This complexity can hinder an LLM’s ability to identify and focus on the most relevant patterns.
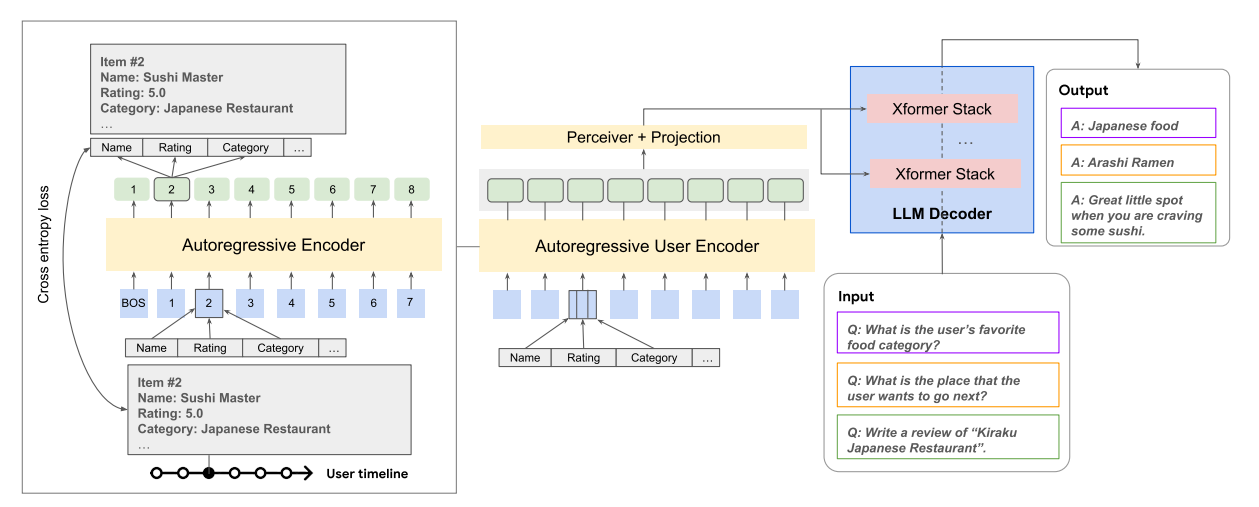
To address these inherent complexities and limitations of leveraging raw user interaction data with LLMs, researchers have proposed USER-LLM, a novel approach centered around user embeddings. USER-LLM dynamically incorporates user preferences and behaviors from various interaction modalities (e.g., video watch history, ratings, location visits), enhancing LLM understanding and personalization capabilities while supporting various encoder architectures and multimodal fusion mechanisms.
The USER-LLM approach consists of two key phases: generating high-quality user embeddings and contextualizing LLMs with these user embeddings. In phase one, a Transformer-based encoder is pretrain on user interaction data, utilizing self-supervised learning to capture behavioral patterns across multiple interaction modalities. Then a multifeature autoregressive Transformer is used to generate embeddings that capture long-range dependencies and contextual relationships within sequential data while handling multimodal user data effectively. In phase two, user embeddings is integrated with an LLM during fine tuning using cross attention, where the LLM’s intermediate text representations attend to the output embeddings from the pretrained user encoder, enabling dynamic context injection (similar to Flamingo).
During experimentation, USER-LLM v.s. DualEnc & Bert4Rec baselines for next item prediction. USER-LLM outperforms the two nonLLM baselines on MovieLens and Google Local review datasets. Overall, USER-LLM showed competitive performance compared with non-LLM baselines and text-prompt-based LLM personalization techniques, particularly in handling long sequences and understanding users deeply.