Multi-modal generative models need to be able to perceive, process, and produce both discrete elements (such as text or code) and continuous elements (e.g. image, audio, and video data). Language models excel with discrete data, such as text, by predicting the next token in a sequence, while diffusion models are best for continuous data, like images. Researchers are working on combining these by integrating diffusion models into language models to enhance performance in both areas.
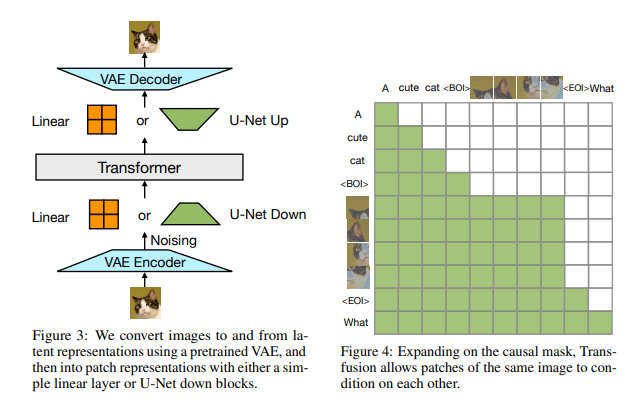
Now researchers have introduced Transfusion, a recipe for training a multi-modal model over discrete and continuous data. Transfusion pretrained a transformer model on 50% text and 50% image data using a different objective for each modality: next token prediction for text and diffusion for images. The model is exposed to both modalities and loss functions at each training step. Standard embedding layers convert text tokens to vectors, while patchification layers represent each image as a sequence of patch vectors. By applying causal attention for text tokens and bidirectional attention for image patches. For inference, a decoding algorithm is used that combines the standard practices of text generation from language models and image generation from diffusion models.
At a high level Transfusion uses a single transformer perceives, processes, and produces data of every modality. Discrete (text) tokens are processed autoregressively and trained on the next token prediction objective. Continuous (image) vectors are processed together in parallel and trained on the diffusion objective. Marker BOI and EOI tokens separate the modalities
Experiments show that Transfusion scales significantly better than quantizing images and training a language model over discrete image tokens. There has been significant performance gain by introducing modality-specific encoding and decoding layers, and even compressing each image to just 16 patches. Further, scaling Transfusion recipe to 7B parameters and 2T multi-modal tokens produces a model that can generate images and text on a par with similar scale diffusion models and language models, reaping the benefits of both worlds.
Paper : https://arxiv.org/pdf/2408.11039