Today’s almost all LLMs are predominantly designed as monolithic architectures, these models rely extensively on large-scale data to embed generalized language capabilities across vast parameter spaces. This makes these LLMs susceptible to forgetting previously learned information when adapted to specialized tasks.
How can we build compositional LLMs that enjoy versatile expertise, while using minimal resources?
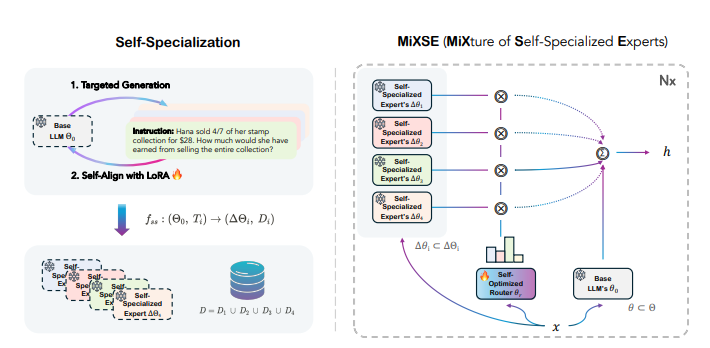
Introducing Self-MoE, an approach that transforms a monolithic model into a compositional modular system of self-specialized experts, called MiXSE (MiXture of Self-specialized Experts). Unlike LoRA, Self-MoE constructs individual lightweight expert modules from scratch using synthetic data. Each module is integrated with the base LLM, and the entire system is enhanced by a self-optimized routing mechanism. This allows for dynamic and capability-specific handling of various target tasks, enhancing overall capabilities, without extensive human-labeled data and added parameters, which LoRA required.
Self-MoE approach to building a compound system of specialized experts and a router in a self-improving manner and done in two phases: In the Self-Specialization phase, the base LLM is aligned with self-generated synthetic data for each target specialization, producing lightweight expert modules. In MiXSE where each self-specialized expert is dynamically engaged based on the decisions of the self-optimized router.
Empirical results show that Self-MoE demonstrates substantial improvements over the base LLM across diverse benchmarks such as knowledge, reasoning, math, and coding. It also consistently outperforms other methods, including instance merging and weight merging, while offering better flexibility and interpretability by design with semantic experts and routing.