Self-correction is a highly desirable capability of large language models (LLMs), yet it has consistently been found to be largely ineffective in modern LLMs. Existing approaches toward self-correcting LLMs either rely on prompt-engineering or fine-tuning models specifically for self-correction, which usually require oracle “teacher” supervision to guide the process of self-correction.
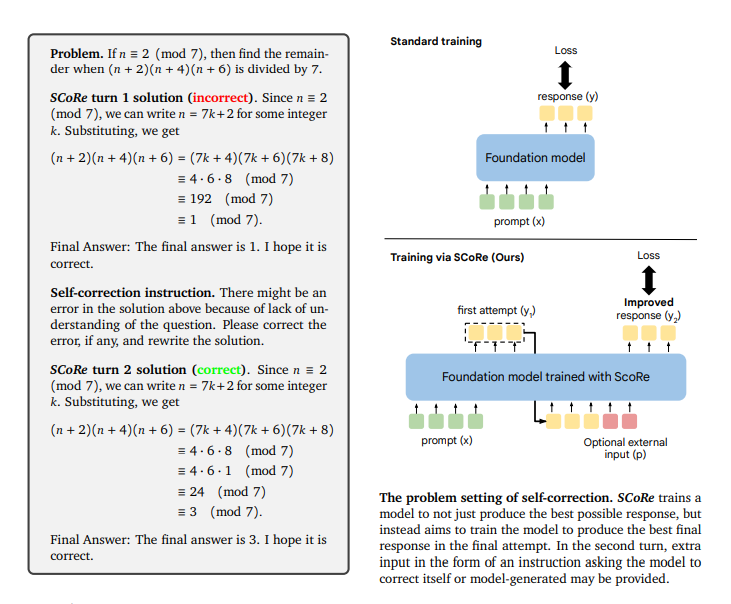
To this end, researchers from Google Deepmind have developed a multi-turn online reinforcement learning (RL) approach, Self-Correction via Reinforcement Learning (SCoRe), which trains only a single model that can both produce a response to a reasoning problem and also correct errors despite not receiving any oracle feedback. More importantly, SCoRe teaches this ability to model entirely by training on self-generated data, without any oracle.
How does SCoRe work? SCoRe tackles the challenges of supervised fine-tuning (SFT) by employing online multi-turn reinforcement learning (RL). It generates its own training data to mitigate distribution mismatches between training and inference. SCoRe is trained in two stages to prevent minimal editing strategies. The first stage optimizes a model initialization focused on correction performance while maintaining closeness to the base model. The second stage employs multi-turn RL to enhance responses, using a reward bonus to incentivize improvements from the first attempt to the second. This approach ensures the model learns to self-correct effectively rather than just slightly editing initial responses.
SCoRe was evaluated on Gemini 1.0 Pro and 1.5 Flash models, achieving state-of-the-art self-correction performance, improving the base models’ self-correction by 15.6% and 9.1% respectively on the MATH and HumanEval benchmarks.
Paper : https://arxiv.org/pdf/2409.12917