Transformer-based large Language Models (LLMs) become increasingly important in various domains. However, the quadratic time complexity of attention operation poses a significant challenge for scaling to longer contexts due to the extremely high inference latency and GPU memory consumption for caching key-value (KV) vectors.
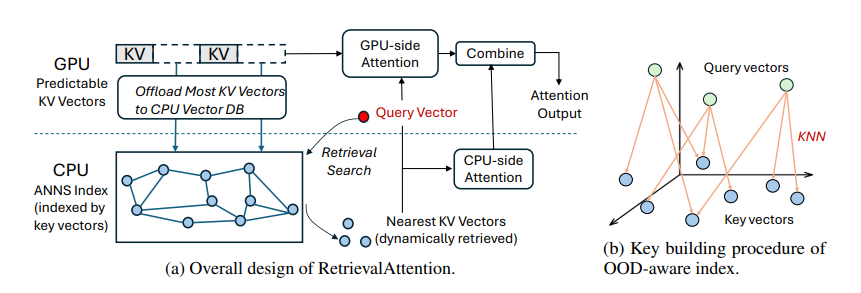
To address this researcher has proposed RetrievalAttention, a training-free approach to accelerate attention computation. To leverage the dynamic sparse property of attention, RetrievalAttention builds approximate nearest neighbor search (ANNS) indexes upon KV vectors in CPU memory and retrieves the most relevant ones via vector search during generation. Due to the out-of-distribution (OOD) between query vectors and key vectors, off-the-shelf ANNS indexes still need to scan O(N) (usually 30% of all keys) data for accurate retrieval, which fails to exploit the high sparsity. RetrievalAttention first identifies the OOD challenge of ANNS-based attention, and addresses it via an attention-aware vector search algorithm that can adapt to queries and only access 1–3% of data, thus achieving a sub-linear time complexity.
To optimize resource utilization, RetrievalAttention retains KV vectors in the GPU memory following static patterns, while offloading the majority of KV vectors to CPU memory for index construction. During token generation, RetrievalAttention efficiently retrieves critical tokens using vector indexes on the CPU and merges the partial attention results from both the CPU and GPU. This strategy enables RetrievalAttention to perform attention computation with reduced latency and minimal GPU memory utilization.
RetrievalAttention were evaluated for accuracy and efficiency on both commodity GPUs (4090) and high-end GPUs (A100) on three long-context LLMs across various long-context benchmarks like ∞-Bench and RULER. For the 128K context on the 4090 GPU, RetrievalAttention achieves 4.9× and 1.98× decoding-latency reduction compared to the retrieval method based on exact KNN and traditional ANNS indexing respectively, while maintaining the same accuracy as full attention. RetrievalAttention only needs 16GB GPU memory for serving 128K tokens in LLMs with 8B parameters, which is capable of generating one token in 0.188 seconds on a single NVIDIA RTX4090 (24GB).
Paper : https://arxiv.org/pdf/2409.10516