The primary objective of retrieval models is to enhance the accuracy of answers by selecting the most relevant documents retrieved for a given query, ensuring models have sufficient information to help the downstream reasoning process. However, there are two major limitations: First, the generative retrieval does not account for contextual information. Secondly, the retrieval can’t be tuned for the downstream readers as decoding the page title is a non-differentiable operation.
Paper introduces Re3val - Reinforced and Reranked Generative Retrieval, a novel framework specifically designed to address the challenges in neural information retrieval. Re3val uses Dense Passage Retrieval (DPR) contexts for reranking retrieved page titles, leading to improved RPrecision. Re3val enhances performance by integrating generated questions in pre-training and utilizing REINFORCE during distant supervision. Moreover, Re3val achieves more accurate answers by reading reranked contexts retrieved with the reranked page titles. These advancements enable Re3val to achieve state-of-the-art performance while also offering cost savings by reducing training time and minimizing the need for extensive data labeling.
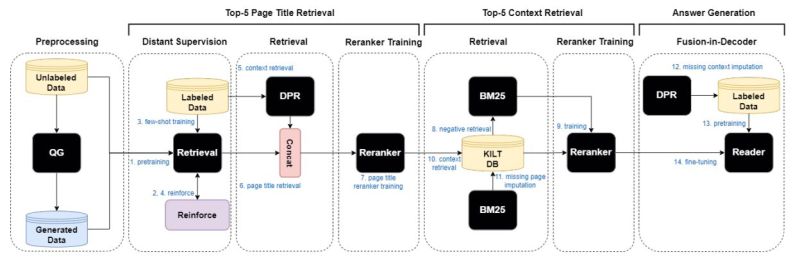
Typical Re3val Training Pipeline consists of the following. Generated questions after filtering are integrated into pre-training (1), followed by few-shot training (3) with REINFORCE (2, 4). Retrieved DPR contexts (5), perturbed page titles (6), and queries are concatenated for reranker training (7). Gold and negative passages retrieved with BM-25 are employed (8) for context reranker training (9). Contexts are retrieved using the top 5 reranked titles from KILT (10), where missing titles are imputed with BM-25 (11). DPR contexts are imputed (12) if lacking five gold contexts during FiD model pre-training (13). FiD model is fine-tuned using five reranked contexts (14).
During inference Reranker concatenates retrieved DPR contexts (1), page titles (2), and query to rerank page titles (3). Contexts retrieved with the top five reranked page titles (4), including BM-25 imputed titles (5), are reranked (6). The top-5 reranked contexts are used to generate an answer (7).
Experimental results demonstrate Re3val’s superiority over the CorpusBrain zero-shot baseline, with an average 8% R-Precision improvement across five tasks using reduced pretraining data. Re3val also achieves an average 1.9% R-Precision increase compared to other generative models via page title reranking with limited taskspecific data. Moreover, by employing a context reranker before grounding, Re3val achieves top-1 KILT scores among generative retrieval models, showing an average 2.1% improvement across five datasets.