Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) is crucial for aligning LLMs with human preferences. While recent research has focused on algorithmic improvements, the importance of prompt-data construction has been overlooked.
To address this gap researchers have started exploring data-driven bottlenecks in RLHF performance scaling, particularly reward hacking and decreasing response diversity and have introduced a hybrid reward system combining reasoning task verifiers (RTV) and a generative reward model (GenRM) to mitigate reward hacking. Further researchers have also proposed a novel prompt-selection method, Pre-PPO, to maintain response diversity and enhance learning effectiveness. Additionally, it was found that prioritizing mathematical and coding tasks early in RLHF training significantly improves performance. Experiments across two model sizes validate these methods’ effectiveness and scalability.
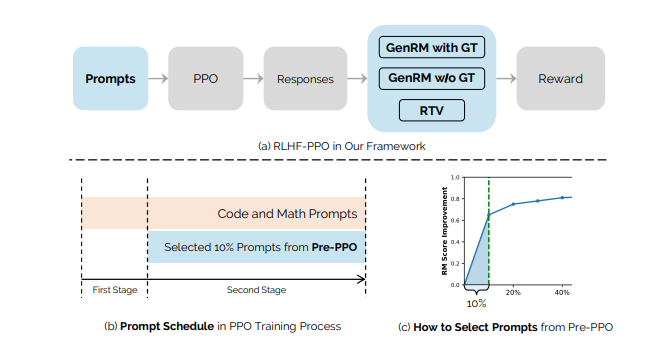
The proposed RLHF pipeline consists of two sequential phases: (1) Reward Model Training, where we construct three complementary reward models—namely, the Bradley-Terry (BT) model, the Generative Reward Model (GenRM), and Reasoning Task Verifiers (RTV). Specifically, the BT model is trained on pairwise comparisons to capture human preferences, while the GenRM assigns explicit reward scores aligned with these preferences using either ground-truth solutions (for reasoning tasks) or the best-of-N selections identified by the BT model (for general tasks). The RTV component implements specialized validators tailored to specific task requirements, such as code-execution sandboxes for evaluating programming tasks; and (2) Reinforcement Learning Optimization, in which the language model is iteratively optimized using PPO under guidance from both GenRM and RTV. This stage leverages carefully selected training prompts identified through our Pre-PPO prompt-selection method and employs strategic optimization techniques to robustly enhance model performance and alignment.
Results show that RTV is most resistant to reward hacking, followed by GenRM with ground truth, and then GenRM with SFT Best-of-N responses. Such strategies enable rapid capture of subtle task-specific distinctions, leading to substantial improvements in overall RLHF performance. This work highlights the importance of careful data construction and provides practical methods to overcome performance barriers in RLHF.
Paper : Exploring Data Scaling Trends and Effects in Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback