Adapting LLMs to the specialized domains, which is essential to many emerging applications, usually takes two paths: in-context learning through Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) and supervised fine-tuning. RAG-based methods allow the Language Model (LLM) to use documents for answering questions but miss out on learning opportunities in fixed domain settings. On other hand, Supervised fine-tuning offers better learning of general document patterns but current approaches don’t effectively use documents during testing or consider retrieval imperfections during training.
So can we adapt pre-trained LLMs for Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) in specialized domains?
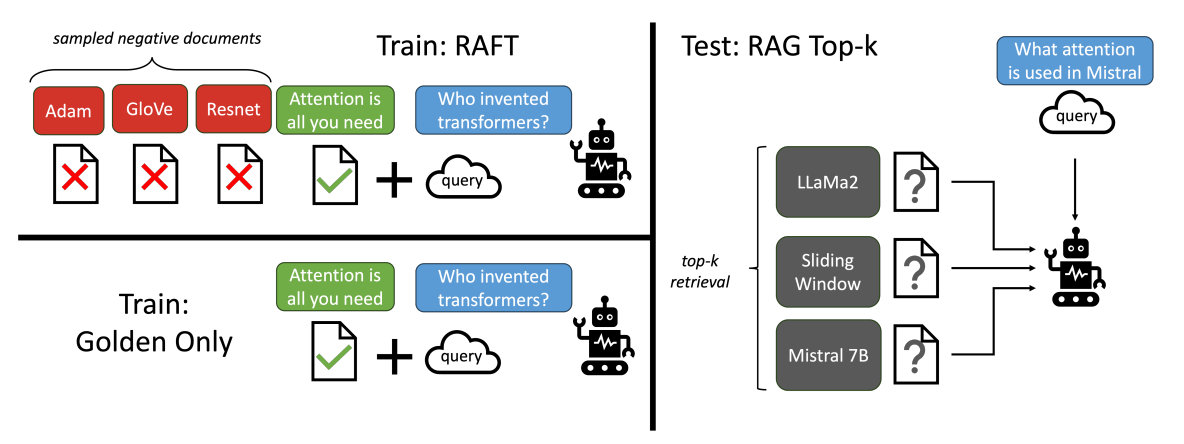
That’s what researchers have tried to address with Retrieval Augmented Fine Tuning (RAFT). RAFT is a training recipe that improves the model’s ability to answer questions in an “openbook” in-domain setting. In RAFT, given a question, and a set of retrieved documents, we train the model to ignore those documents that don’t help in answering the question, which we call, distractor documents. RAFT accomplishes this by citing verbatim the right sequence from the relevant document that would help answer the question. This coupled with RAFT’s chain-of-thought (COT) style response helps improve the model’s ability to reason.
Compared with the base Llama2 instruction-tuned model, RAFT train model with RAG does much better in terms of extracting information as well as being robust towards distractors. The gain can be as big as 35.25% on Hotpot QA and 76.35% on Torch Hub evaluation. Compared with DSF (domain specific finetuning) on the specific dataset, RAFT does much better on tasks like HotpotQA and HuggingFace datasets (30.87% on HotpotQA and 31.41% on HuggingFace). Overall, RAFT presents a novel, yet simple technique to improve pretrained LLMs for in-domain RAG.