Recently, considerable research work has been going towards reducing high computational cost and memory footprint of LLMs, especially during the inference stage. Sparsity is one of the promising approaches among all. Sparsity in LLMs can be used as weight sparsity, which prunes the model weights to save the computation or activation sparsity, which reduces the number of activated elements in the activation tensors. However there are challenges associated with sparsity in terms of model accuracy and efficiency again.
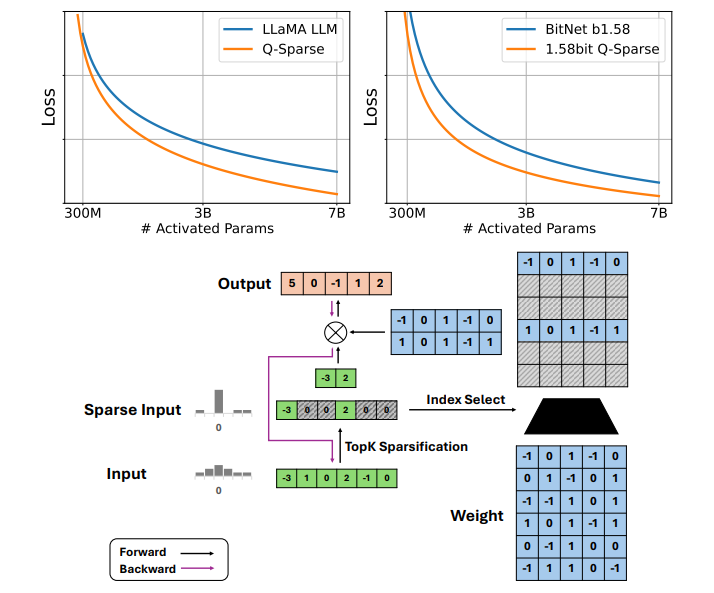
In order to address these issues and also study the full impact of sparsity researchers have introduced Q-Sparse, a simple yet effective approach to enable full sparsity of activations in LLMs. The major modification on LLMs is in the linear projection (i.e., matrix multiplication). For each linear projection, it has a top-K sparsification function that selects the top-K activations in the input tensor.
Y = (X ⊙ M) · WT (2)
M = Topk (|X|) (3)
where M ∈ R N×D is the mask tensor that indicates the top-K activations in the input tensor X in terms of the absolute values, ⊙ is the element-wise multiplication operation, and Top k is the function that selects the top-K elements in the tensors.
For the backpropagation, the straight through estimator is used to compute the gradients of the activations. Further, a squared ReLU function is also used for the feed-forward layers to further improve the sparsity of the activations. Q-Sparse can be used with both full-precision and quantized LLMs. To study the scaling law of sparsely-activated LLMs, we conduct a series of scaling experiments and derive an inference-optimal scaling law for sparsely-activated LLMs.
Q-Sparse LLMs were evaluated under various settings, including training from scratch, continue-training, and fine-tuning. When training from scratch with 50B tokens, Q-Sparse matched dense baselines at 40% sparsity. BitNet b1.58 models with Q-Sparse outperformed dense baselines with the same compute budget. Fine-tuning results demonstrated that Q-Sparse models with around 4B activated parameters matched or exceeded the performance of dense 7B models, proving Q-Sparse’s efficiency and effectiveness across training scenarios.
Paper : https://arxiv.org/pdf/2407.10969