Evaluating language models is a challenging task: not only is it difficult to find meaningful data to test the models, but evaluating the correctness of a generated response is itself a challenge. You will find that LLM evaluation benchmark tests such as MMLU or automatic evaluation metrics such as BLEU score for machine translation and ROUGE for summarization commonly fail to analyze the intended property of interest.
Recently, model-based scoring or LLM “as Judge” found to be performing better than above heuristic metrics. However, using LLMs like GPT4 for evaluation tend to have their own biases; often recognizing and preferring their own outputs over those of other models and also much more expensive.
So is there any better way to automatically evaluate LLMs?
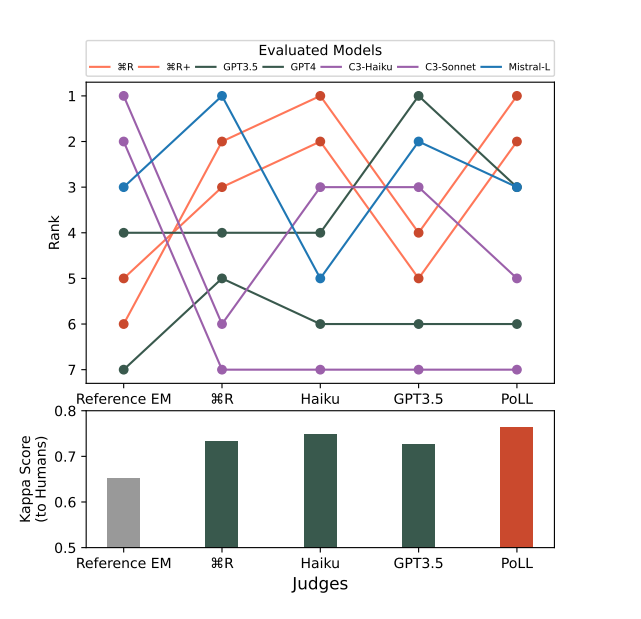
Cohere has come up with a new approach called Panel of LLm evaluators (PoLL) that replaces a single LLM “as Judge” with multiple LLMs “Juries” and uses vote to get the best result. PoLL consists of a larger number of smaller models called Juries and a voting function to aggregate the score across these Juries and finally Cohen’s Kappa correlation is used to compare results with human preferences.
During experimentation, a PoLL was constructed from three models drawn from three disparate model families (Command R, Haiku, and GP 3.5). Further, two different voting functions for aggregating scores across the judges were used. For QA datasets, max voting was used as all judgements are binary [correct, incorrect]. For Chatbot Arena average pooling methods were used because judgements are scores ranging from 1-5 and a three judge panel often does not produce a clear majority decision. Finally, Cohen’s Kappa correlations were used to compare results with human preferences. Cohen’s kappa Correlation measures inter-rater reliability, which quantifies the level of agreement between two or more raters or judges.
PoLL outperforms single judges (GPT-4) across multiple datasets, exhibits less intra-model bias due to its composition of disjoint model families, and does so while being over seven times less expensive (7-8x cheaper than GPT-4).
Paper : https://arxiv.org/pdf/2404.18796