Despite the recent advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs), which have significantly enhanced the generative capabilities for various NLP tasks, LLMs still face limitations in directly handling retrieval tasks. However, many practical applications demand the seamless integration of both retrieval and generation.
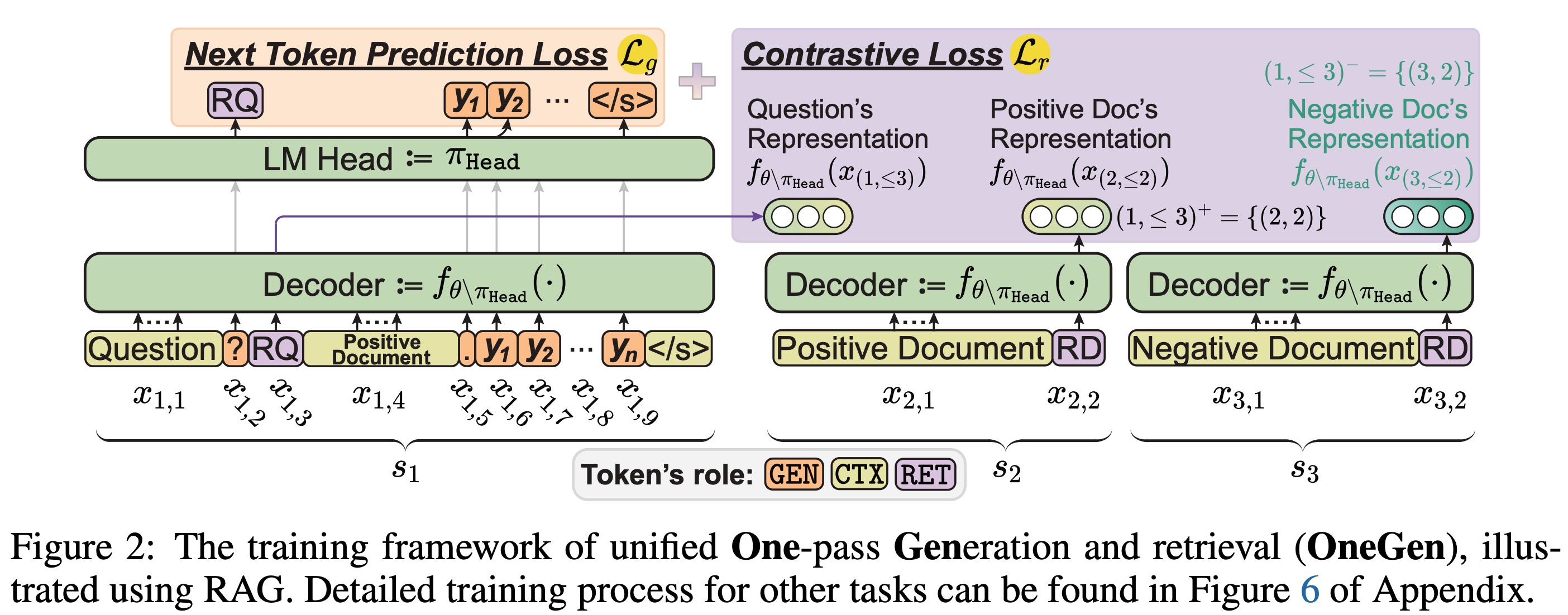
To address this researchers have introduced a novel and efficient One-pass Generation and retrieval framework (OneGen), designed to improve LLMs’ performance on tasks that require both generation and retrieval. The proposed framework bridges the traditionally separate training approaches for generation and retrieval by incorporating retrieval tokens generated autoregressive. This enables a single LLM to handle both tasks simultaneously in a unified forward pass.
OneGen uses special tokens called retrieval tokens and allocates the retrieval task to retrieve tokens generated in an autoregressive manner. During training, retrieval tokens only participate in representation fine tuning through contrastive learning, whereas other output tokens are trained using language model objectives. At inference time, retrieval tokens are used for efficient retrieving on demand.
OneGen was evaluated on two distinct types of composite tasks, RAG and Entity Linking, to validate the pluggability, effectiveness, and efficiency of OneGen in training and inference. Furthermore, results show that integrating generation and retrieval within the same context preserves the generative capabilities of LLMs while improving retrieval performance. Thus making OneGen first of its kind to enable LLMs to conduct vector retrieval during the generation.
Paper : https://arxiv.org/pdf/2409.05152