LLMs have been effective in a wide range of applications, yet the most sophisticated models are often proprietary (GPT 4, Gemini) and considerably costly than open source ones. However, recently niche-specific smaller language models, such as those tailored for legal, medical or financial tasks, have outperformed their proprietary counterparts considerably.
Is there any way to integrate all these LLMs in order to manage multiple downstream tasks without compromising performance and staying within budget?
That is what researcher from nexa4ai has done with Octopus v4, a novel approach that employs functional tokens to integrate multiple open-source models, each optimized for particular tasks. Octopus v4 model leverages functional tokens to intelligently direct user queries to the most appropriate vertical model and reformat the query to achieve the best performance.
The architecture consists of two abstraction layers. The first layer utilizes functional tokens to represent the actions executable by the Octopus v2 model. This layer encompasses three distinct Octopus v2 models, each identified by different functional tokens, effectively differentiating them as separate AI agents. The second layer of abstraction pertains to the Octopus v4 model, where internal functional tokens are mapped to various v2 models.
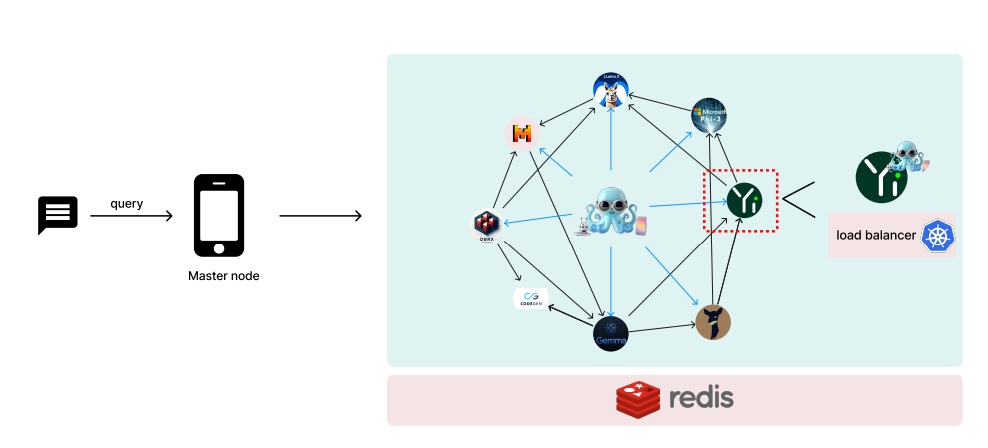
Framework features a graph of language models with a master node deployed on a central device and worker nodes distributed across various devices. Kubernetes (k8s) is employed for serverless deployment of each individual worker language model. For efficient data sharing, a distributed cache mechanism supported by Redis is used. Note that for each worker node, a small Octopus v4 Lora is attached to guide it to the next neighbor node for the case of multi-Agent use cases. During evaluation it was found that the model achieved a SOTA MMLU score of 74.8 among the same 10B level models.
Paper : https://arxiv.org/pdf/2404.19296