For Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs), scaling the model can effectively improve performance. However, expanding model parameters significantly increases the training and inferring costs, as all model parameters are activated for each token in the calculation.
In contrast, sparse Mixtures of Experts (MoE) effectively scale model capacity by using fixed activated parameters to process data, which has thrived in the field of NLP . Recently, Mistral LLM equipped with the MoE layers has gained popularity in LLMs. Mixtral-MoE8×7B achieves performance comparable to LLaMA 2-70B with fewer computational resources.
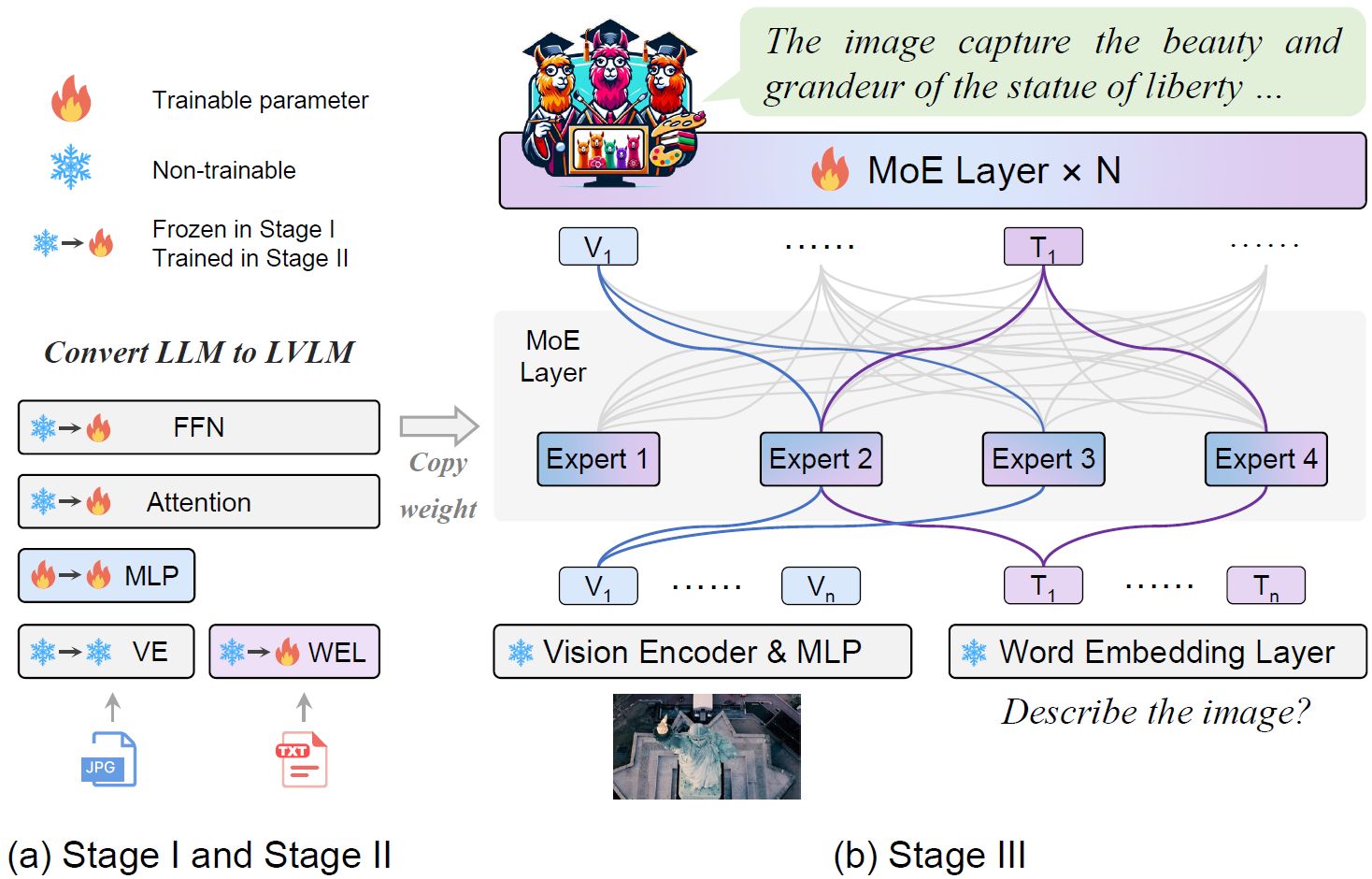
However, directly applying MoE to train sparse LVLMs is challenging as it leads to significant performance degradation. Proper initialization is crucial for sparsifying the LVLM, and that’s exactly what MoE-tuning does. MoW-tuning - a novel three-stage training strategy for adapting MoE to LVLMs and preventing the model degradation caused by sparsity.
MoE-LLaVA model operates by using multiple sparse paths, where each token is directed to different experts through a router. These activated experts collaboratively process the tokens, while inactive paths remain dormant. By stacking MoE encoder layers iteratively, the model creates a sparse pathway to a larger and more potent Large Vocabulary Language Model (LVLM). This approach allows for efficient and effective processing of input data by dynamically routing tokens to appropriate experts for processing.
During experimentation MoELLaVA model demonstrates great potential for multi-modal understanding and hallucination inhibition. MoELLaVA achieves comparable performance to state-of-the-art 7B models with only 3B sparse activated parameters on multiple visual understanding datasets, and outperforms LLaVA-1.5-13B by 1.1% on the POPE hallucination benchmark with 2.2B activated parameters.
Paper : https://arxiv.org/pdf/2401.15947.pdf
@article{lin2023video,
title={Video-LLaVA: Learning United Visual Representation by Alignment Before Projection},
author={Lin, Bin and Zhu, Bin and Ye, Yang and Ning, Munan and Jin, Peng and Yuan, Li},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2311.10122},
year={2023}
}