Following the success of the instruction-tuned LLMs, several visual instruction tuning datasets have been meticulously curated to enhance zero-shot vision language (VL) performances in large language and vision models (LLVMs). Due to this several open-source LLVMs such as InstructBLIP, Owen-VL and LLaVA1.5 have been closing the gap in zero-shot VL performances compared to closed-source LLVMs such as GPT-4V, Gemini-Pro, and Qwen-VL-Plus.
However, current LLVMs have disregarded the detailed and comprehensive real-world scene understanding available from specialized computer vision (CV) models in visual perception tasks such as segmentation, detection, scene graph generation (SGG), and optical character recognition (OCR). Instead, the existing LLVMs rely mainly on the large capacity and emergent capabilities of their LLM backbones.
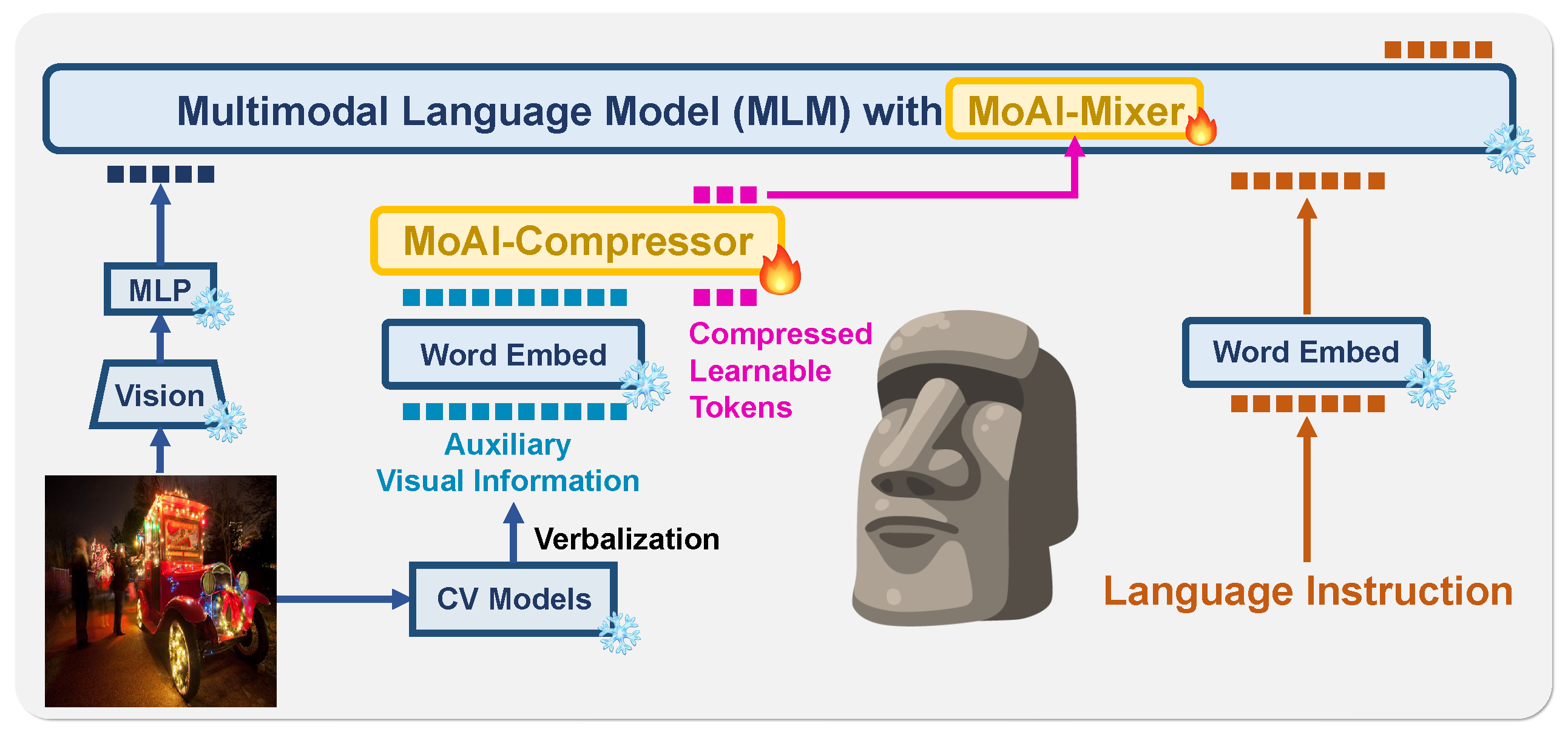
In light of this, researcher propose a new LLVM, Mixture of All Intelligence ( MoAI), which leverages auxiliary visual information obtained from various sources: (1) panoptic segmentation , (2) open-world object detection, (3) SGG, and (4) OCR models. To effectively leverage this information, two new modules are introduce: MoAI-Compressor and MoAI-Mixer. The MoAI-Compressor aligns and condenses the verbalized outputs of the external CV models into auxiliary visual information, enabling the efficient use of relevant information for VL tasks. Subsequently, MoAI-Mixer blends three types of intelligence—(1) visual features, (2) auxiliary features from external CV models, and (3) language features—into a cohesive whole.
During experimentation, MoAI-7B surpasses the zero-shot performances, despite being relatively small compared to the considerably larger open-source (InstructBLIP, Owen-VL and LLaVA1.5) and closed source models (GPT-4V, Gemini-Pro, and Qwen-VL-Plus). Notably, those related to real-world scene understanding such as object existence, positions, relations, and OCR without enlarging the model size or curating extra visual instruction tuning datasets. MoAI performs well even on hallucination zero-shot datasets: POPE and HallusionBench, which suggests that accurately recognizing objects and their relationships can help prevent LLVMs from making mistakes.
Paper : https://arxiv.org/pdf/2403.07508.pdf