Adapter-based fine-tuning methods, such as LoRA, are key to making large language models disruptive in various domain specific applications. LoRA introduces a limited number of domain-specific parameters to retain domain related knowledge and does not need to fine-tuning all parameters of the pre-trained model, which can effectively reduce the training cost of LLMs.
So is it possible to obtain multiple customized domain capabilities from a single LLM model with LoRA?
Simple approach would be to directly mix data from multiple domains together and only add one LoRA module for instruction fine-tuning. However, achieving the right balance of data is crucial in such a case in order to prevent catastrophic forgetting and interference between tasks.
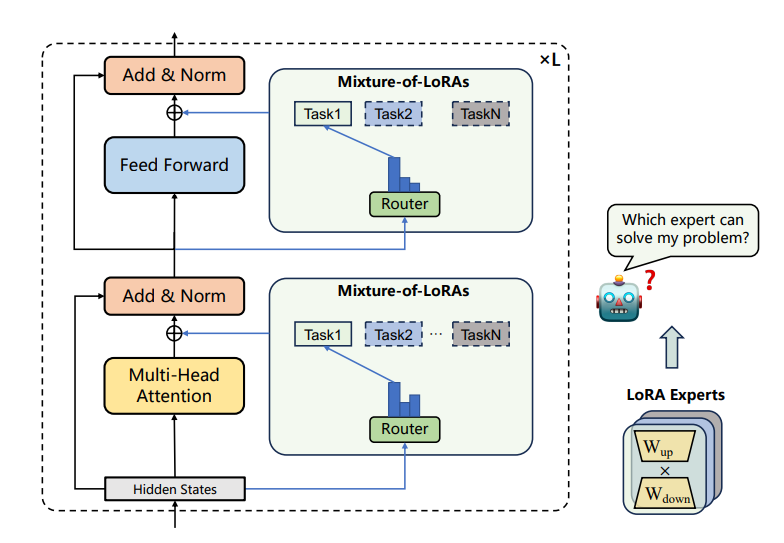
To address these limitations and enhance training flexibility, researchers propose the Mixture-of-LoRAs (MoA) architecture – a novel and parameter-efficient tuning method designed for multi-task learning with LLMs. MoA introduces a routing mechanism within a decoder-only model architecture to automatically select LoRA experts. This mechanism is applicable to mainstream Large Language Models (LLMs) and can deploy LoRA modules for multiple tasks using the same LLM while managing limited computing resources. Additionally, To enhance training and inference efficiency, MoA employs parallel processing of different domain samples within a batch during training and a LoRA expert selection approach during inference. This approach harnesses the strengths of different expert models and the base LLM while leveraging the complementary nature of knowledge across different domains.
Experiments on diverse domain specific tasks such in Finance, Medicine, Stackoverflow and leetcode have demonstrate that MoA outperform both single LoRA and single-LoRA mix in teams of PPL, BLUE and ROUGE-L (Perplexity: 4.0128→3.9450, BLUE: 28.5348→30.5912, ROUGE-L: 37.7877→39.0163), which will also further promote the application of domain specific LLMs.