In the traditional RAG framework, the basic retrieval units are normally short but the retriever needs to scan over a massive amount of units to find the relevant piece. Such an imbalanced puts too much pressure on the retriever, which needs to recall a huge amount of units, such as the top-100 or even more, combined with additional complex re-ranker to achieve great performance. Moreover, short retrieval units can lead to semantic incompleteness due to document truncation. This can lead to information loss, ultimately restricting the end performance.
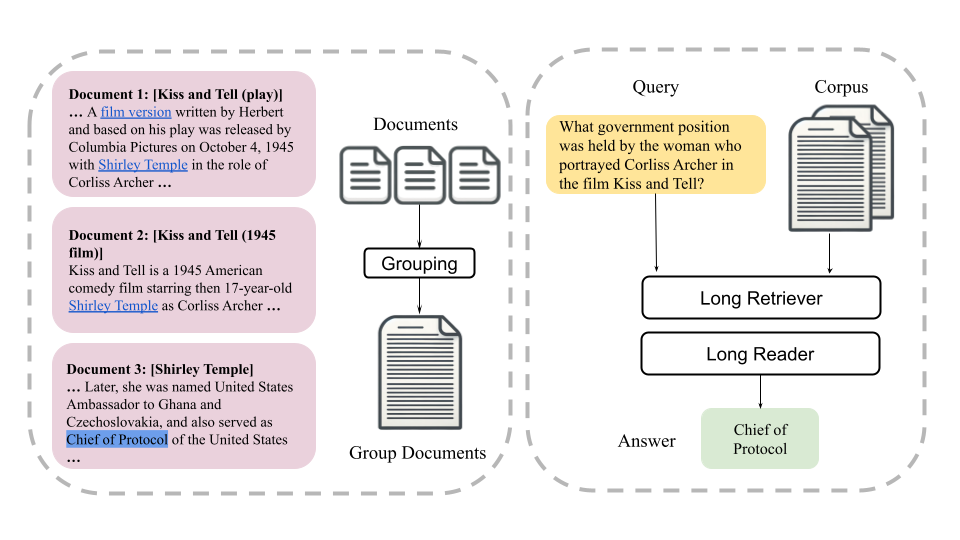
In order to alleviate the imbalance, a new framework is proposed called LongRAG, which places greater emphasis on recall, aiming to retrieve relevant context with much coarse granularity. This shifts more burden from the retriever to the reader to extract the exact answers from the relevant context.
LongRAG consists of two components: the “long retriever” and the “long reader”. Long Retriever will identify coarse relevant information for the given query by searching through all the long retrieval units in the corpus. The top 4 to 8 retrieval units are concatenated as the retrieved long context for the next step.
Long Reader, here long reader will further extract answers from the concatenation of retrievals, which is normally around 30K tokens. Finally, a simple prompt is used with an existing long-context LM (like Gemini or GPT4) with the question to produce the answers.
LongRAG processes the entire Wikipedia into 4K-token units, which is 30x longer than before. By increasing the unit size, it significantly reduces the total units from 22M to 600K. This significantly lowers the burden of retriever, which leads to a remarkable retrieval score: answer recall@1=71% on NQ (previously 52%) and answer recall@2=72% (previously 47%) on HotpotQA (full-wiki).
Then the top-k retrieved units (≈ 30K tokens) are fed to an existing long-context LLM to perform zero-shot answer extraction. Without requiring any training, LongRAG achieves an EM of 62.7% on NQ and 64.3% on HotpotQA (full-wiki), which is on par with the SoTA model. Our study offers insights into the future roadmap for combining RAG with long-context LLMs.
Paper : https://arxiv.org/pdf/2406.15319