Recent advancements in text-to-video (T2V) generative models have shown impressive capabilities. However, these models are still inadequate in aligning synthesized videos with human preferences, which is particularly difficult to address, as human preferences are inherently subjective and challenging to formalize as objective functions.
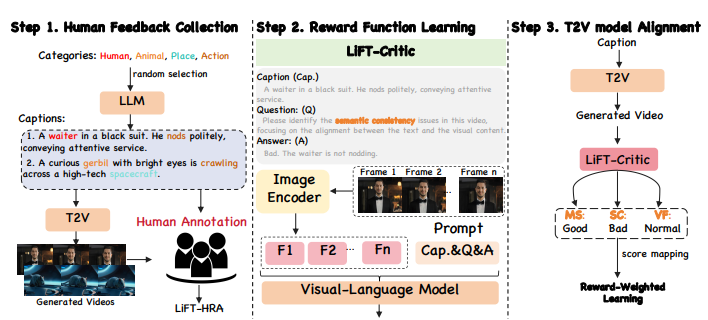
To address this researchers have proposed LIFT, a novel fine-tuning method leveraging human feedback for T2V model alignment. At the core LIFT fine-tuning pipeline consist of three key steps of our: (1) Human Feedback Collection: Where it generate video-text pairs using prompts expanded from random category words with an LLM, then annotate them to create LIFT-HRA. (2) Reward Function Learning: a visual-language model LIFT-CRITIC, is trained to predict human preference scores across three dimensions, learning the reward function from the dataset. (3) T2V Model Alignment: LIFT-CRITIC evaluates the T2V-generated videos, assigns scores, and maps them into a reward weight to fine-tune the T2V model, aligning it with human preferences.
Further, researchers have constructed a Human Rating Annotation dataset, LIFTHRA, consisting of approximately 10k human annotations, each including a score and its corresponding reason. Based on this, a reward model LIFT-CRITIC is trained to learn reward function effectively, which serves as a proxy for human judgment, measuring the alignment between given videos and human expectations. Lastly, the learned reward function is then leveraged to align the T2V model by maximizing the reward-weighted likelihood.
As a case study, researchers apply LIFT pipeline to CogVideoX-2B, showing that the fine-tuned model outperforms the CogVideoX-5B across all 16 metrics, highlighting the potential of human feedback in improving the alignment and quality of synthesized videos.
Paper : LiFT: Leveraging Human Feedback for Text-to-Video Model Alignment