Standard prompt-based LLM inference has two sequential stages: prefilling and decoding. During the prefilling stage, the model computes and saves the KV cache of each token from the prompt, and predicts the first token and time taken during prefilling stage is usually referred as “time-to-first-token” (TTFT). During the decoding stage, the model reuses cached KVs to decode the next token iteratively until the stop criteria are met.
For long prompts, the KV cache must be computed for all tokens during the prefilling stage, which can significantly increase TTFT. Consequently, the prefilling stage may become a bottleneck in the generation process
One may ask, are all prompt tokens essential for generating the first token ?
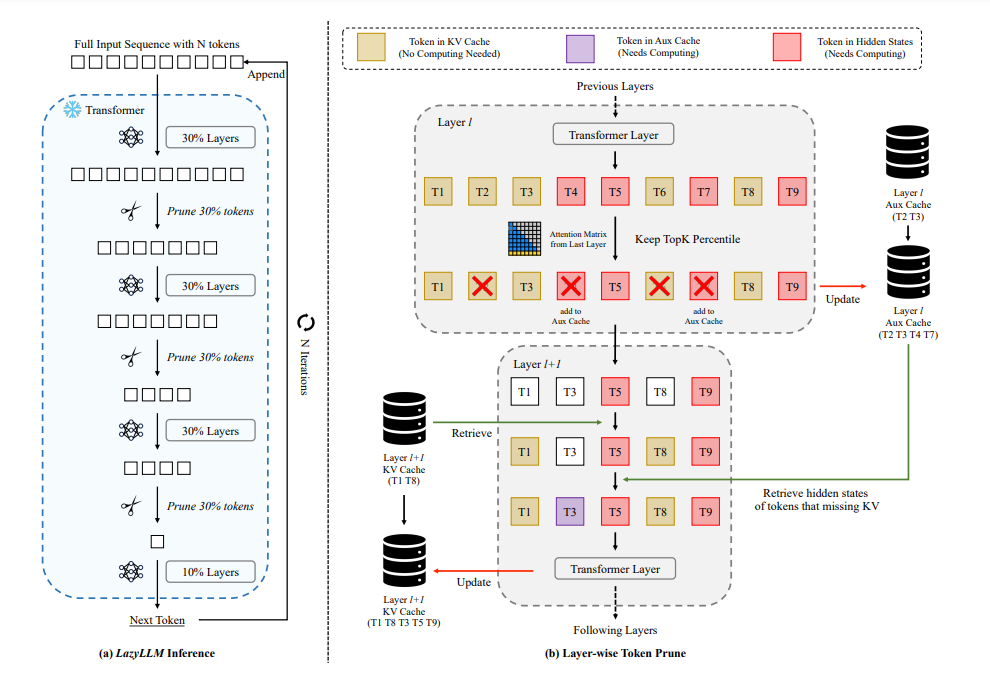
To answer this, researcher have introduce LazyLLM, a novel method that selectively computes the KV for tokens important for the next token prediction in both the prefilling and decoding stages. Contrary to static pruning approaches that prune the prompt at once, LazyLLM allows language models to dynamically select different subsets of tokens from the context in different generation steps, even though they might be pruned in previous steps.
LazyLLM starts with the full context and progressively prunes tokens to gradually reduce the number of computations towards the end of the model. LazyLLM allows the model to select different subsets of tokens from the context in different generation steps.
As comparison to standard LLM, which compute the KV cache of all input tokens at the prefilling stage, LazyLLM only selectively computes the tokens that are important to the next token prediction, deferring the computation of remaining tokens to later steps. LazyLLM significantly optimizes TTFT by reducing the amount of computation during prefilling. Moreover, as some tokens in the prompt are never selected by LazyLLM during the whole generation process. Moreover LazyLLM also reduces the total amount of computation and accelerates the overall generation.
Extensive experiments on standard datasets across various tasks demonstrate that LazyLLM is a generic method that can be seamlessly integrated with existing language models to significantly accelerate the generation without fine-tuning. For instance, in the multi-document question-answering task, LazyLLM accelerates the prefilling stage of the LLama 2 7B model by 2.34× while maintaining accuracy.
Paper : https://arxiv.org/pdf/2407.14057