Optimizing LLMs operational cost and computation requirement is one of the sortout topics for researchers. Accelerated solutions deploy on mobile, edge devices or commodity GPUs such as laptops do exist but they suffer from significant drop in accuracy since a large portion of these LLM acceleration approaches focus on reducing the number of non-zero weights, number of bits per weight or number of heads per layer.
So is there any way we can deploy accelerated LLMs solutions economically without sacrificing accuracy ?
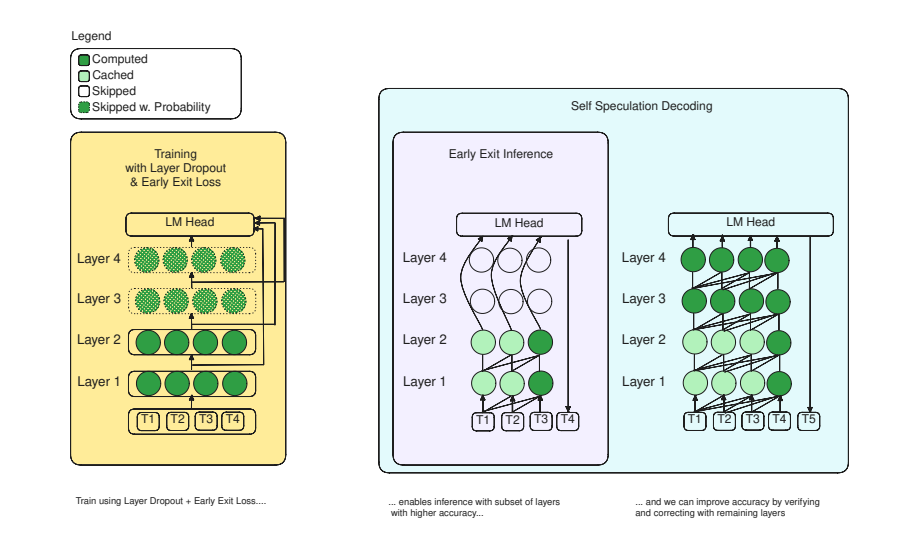
To address this AI @ Meta has introduced the LayerSkip method, an end-to-end solution to speed-up inference of large language models (LLMs), which reduces the number of layers required for each token by exiting early during inference. Unlike quantization or sparsity, acceleration by reducing the number of layers does not require specialized hardware or software kernels. LayerSkip solution work as follow
First, during training layer dropout is applied, with low dropout rates for earlier layers and higher dropout rates for later layers, and an early exit loss where all transformer layers share the same exit.
Second, during inference, the training recipe increases the accuracy of early exit at earlier layers, without adding any auxiliary layers or modules to the model.
Third, a self-speculative decoding novel solution is utilize where it exists at early layers and verifies and corrects with remaining layers of the model.This self-speculative decoding approach has less memory footprint than other speculative decoding approaches and benefits from shared compute and activations of the draft and verification stages.
During evaluation experiments were run on different Llama model sizes on different types of training: pretraining from scratch, continual pretraining, finetuning on specific data domain, and finetuning on specific task. LayerSkip inference solution have show speedups of up to 2.16× on summarization for CNN/DM documents, 1.82× on coding, and 2.0× on TOPv2 semantic parsing tasks.
Paper : https://lnkd.in/dWNjW52i