Large Language Models (LLMs) have been instrumental in pushing innovation across multiple domains. However, despite these advancements, the current LLM paradigm encounters challenges and limitations in data science applications, particularly in domains that demand extensive expertise and advanced coding knowledge.
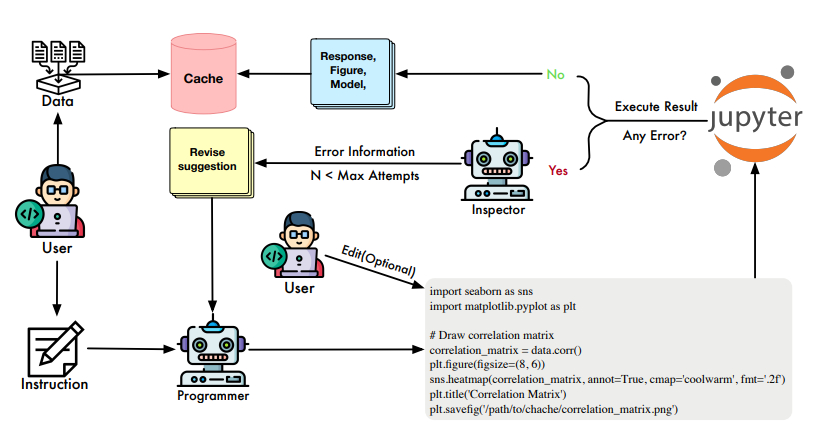
To address this researchers have introduced LAMBDA (A Large Model Based Data Agent), a novel open-source, code-free multi-agent data analysis system. LAMBDA is designed to address data analysis challenges in complex data-driven applications through the use of innovatively designed data agents that operate iteratively and generativity using natural language.
At the core of LAMBDA are two key agent roles: the programmer and the inspector, which are engineered to work together seamlessly. Specifically, the programmer generates code based on the user’s instructions and domain-specific knowledge, enhanced by advanced models. Meanwhile, the inspector debugs the code when necessary. To ensure robustness and handle adverse scenarios, LAMBDA features a user interface that allows direct user intervention in the operational loop. Additionally, LAMBDA can flexibly integrate external models and algorithms through knowledge integration mechanisms, catering to the needs of customized data analysis.
LAMBDA demonstrates superior performance on various machine learning (ML) datasets. Notable results with an accuracy of 100%, 98.07%, and 98.89% on datasets NHANES, Breast Cancer, and Wine respectively. To sum up, the main characteristics of LAMBDA are as follows: (1) Codingfree and natural language interface. (2) Integrating human intelligence and AI. (3) Reliability. (4) Automatic analysis report generation.
Paper : https://arxiv.org/pdf/2407.17535