Recently, the ability to follow complex instructions with multiple constraints is gaining increasing attention as LLMs are deployed in sophisticated real-world applications. However, most benchmarks lay emphasis on evaluating LLMs’ ability to follow complex instructions, and lack of algorithms tailored for enhancing the corresponding ability.
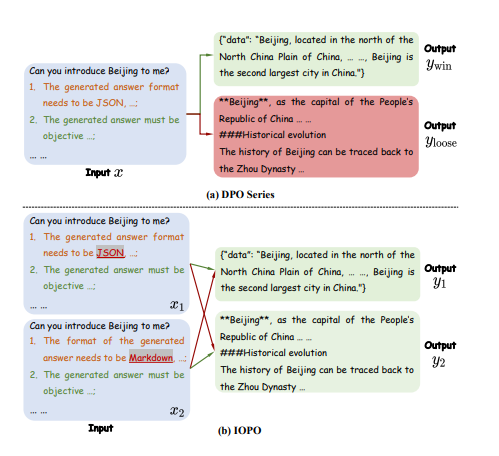
To address this researchers have introduced IOPO (Input-Output Preference Optimization), a novel technique to empower large language models (LLMs) with complex instruction following capabilities. Typically, LLMs are trained on a massive amount of text data, which allows them to become very capable at generating human-like text. However, this training process doesn’t necessarily ensure that the model will behave in alignment with human values and preferences when given complex instructions.
IOPO tries to address this by explicitly optimizing the LLM’s preferences during training. The researchers collect information about what users consider “good” or “desirable” responses to certain inputs, and then use this to guide the model’s training. This helps the LLM learn to prioritize outputs that are more aligned with human preferences.
The core innovation of IOPO is to optimize the LLM’s preferences over input-output pairs during training, rather than just maximizing the likelihood of the training data. This is achieved through a two-stage training process: 1. Preference Collection: The researchers first collect information about user preferences for different input-output pairs, using techniques like FIPO and Triple Preference Optimization. 2. Preference Optimization: The LLM is then trained using a novel objective function that encourages the model to generate outputs that are more aligned with the collected user preferences. This is implemented through direct preference optimization techniques.
Extensive experiments on both in-domain and out of-domain datasets confirm the effectiveness of IOPO, showing 8.15%, 2.18% improvements on in-domain data and 6.29%, 3.13% on out of-domain data compared to SFT and DPO respectively.
Paper : IOPO: Empowering LLMs with Complex Instruction Following via Input-Output Preference Optimization