These days the training context windows of many contemporary LLMs have been expanded to tens of thousands of tokens, thereby enabling these models to process extensive context as input. However, recent studies have revealed that these long-context LLMs struggle to effectively and robustly utilize all the information provided in the context, known as the lost-in-the-middle challenge. This mainly stems from insufficient explicit supervision during the long-context training, which fails to emphasize that any position in a long context can hold crucial information.
So how can we make long-context LLMs fully utilize the information in the long context?
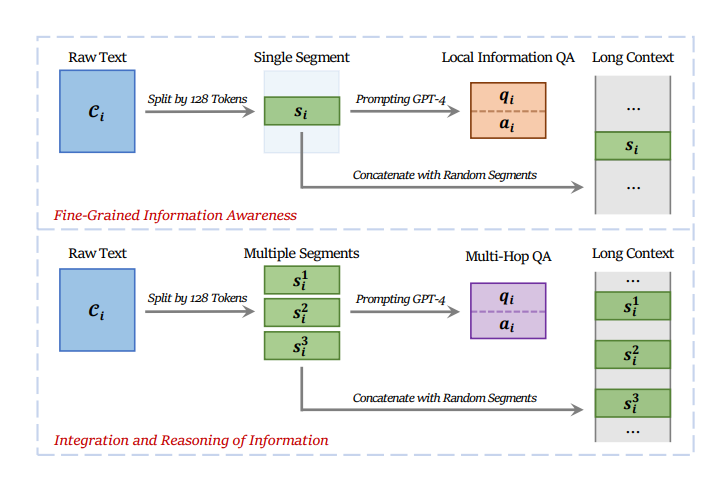
To address this researchers have introduced INformation-INtensive (IN2) training, a purely data-driven solution to overcome lost-in-the-middle. The IN2 training aims to explicitly teach the model that any position in a long context can contain crucial information. To achieve this goal, a long-context question-answer training dataset D = {Li , qi , ai}, is constructed based on a general natural language corpus C where the answer ai to the question qi requires the information contained in some short segments (∼128 tokens) that are randomly placed in the whole long context Li (ranging from 4K to 32K tokens). Two types of question-answer pairs are generated which require (1) the awareness of fine-grained information in the long context, and (2) the integration and reasoning of information appearing at different positions in the long context.
During experimentation IN2 training method was applied on Mistral-7B model with realnewslike subset from the C4 corpus as training corpus, and GPT-4-Turbo as the stronger LLM to generate QA pairs and a new model was introduce called FILM-7B (FILlin-the-Middle). Further, FILM-7B was evaluated on three probing tasks that encompass various context styles (document, code, and structured-data context) and information retrieval patterns (forward, backward, and bi-directional retrieval). The probing results demonstrate that FILM-7B can robustly retrieve information from different positions in its 32K context window. Beyond these probing tasks, FILM-7B significantly improves the performance on real-world long-context tasks (e.g., 23.5→26.9 F1 score on NarrativeQA), while maintaining a comparable performance on short-context tasks (e.g., 59.3→59.2 accuracy on MMLU).
Paper : https://arxiv.org/pdf/2404.16811