All text-based language problems can be reduced to either generation or embedding. Creating a single general model that performs such a wide range of tasks has been a long-standing goal. Recently, large language models (LLMs) have emerged as a promising direction for a single multi-task model.
So can we train an unified LLM which is equally good both in generation and embedding tasks ?
Introducing generative representational instruction tuning (GRIT) whereby a large language model is trained to handle both generative and embedding tasks by distinguishing between them through instructions. GRIT combines this two previously disjoint training paradigms by: (1) Generative instruction tuning, whereby the model is trained to respond to instructions by generating an answer and (2) Representational instruction tuning, whereby the model is trained to represent a provided input according to an instruction Via the instructions and separate loss functions the model learns to differentiate the two streams.
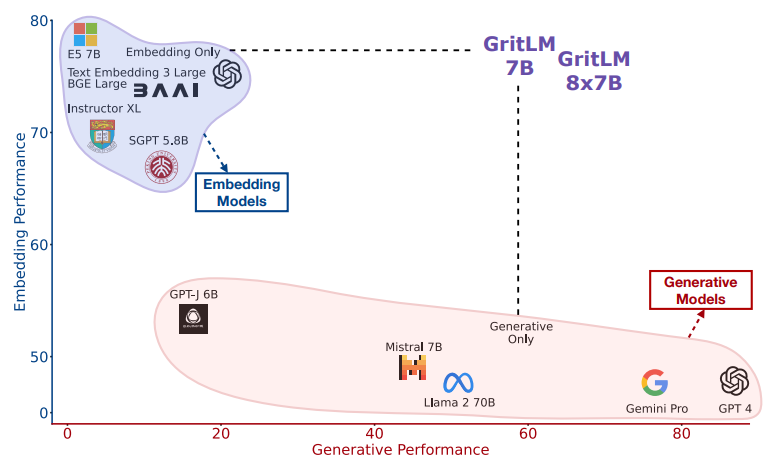
Compared to other open models, resulting LLM trained with GRIT - GRITLM 7B sets a new state of the art on the Massive Text Embedding Benchmark (MTEB) and outperforms all models up to its size on a range of generative tasks. By scaling up further, GRITLM 8X7B outperforms all open generative language models that we tried while still being among the best embedding models. Notably, it was found that GRIT matches training on only generative or embedding data, thus unifying both at no performance loss. Among other benefits, the unification via GRIT speeds up Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) by > 60% for long documents, by no longer requiring separate retrieval and generation models.