Recently, diffusion models (DiT) have emerged as powerful deep generative models in various domains, such as image, video and 3D objects. However, training and serving such models is expensive. This is partially because these deep networks are typically dense. Various techniques are used to address this issue and a sparse mixture of experts (MoE) are becoming increasingly popular among them as a practical implementation that employs a routing mechanism to control computational costs.
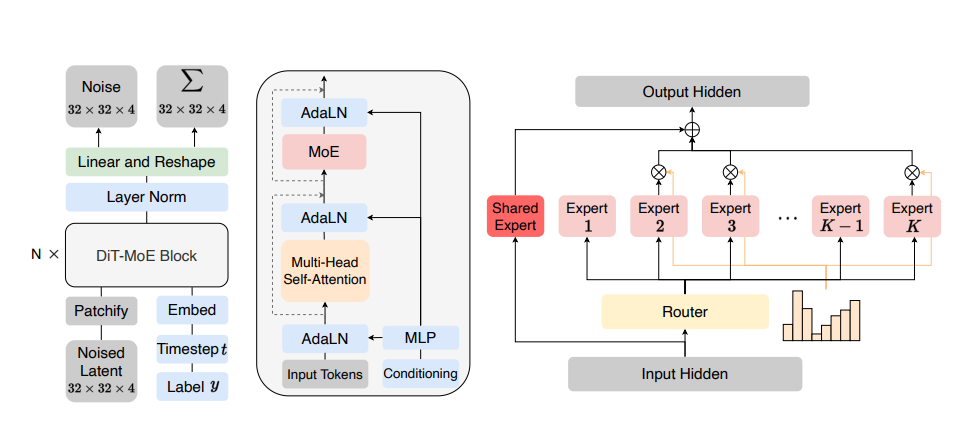
Now researchers have proposed DiT-MoE, a sparse variant of the DiT architecture that is scalable and competitive with dense networks while exhibiting highly optimized inference. The DiT-MoE replaces a subset of the dense feedforward layers in DiT with sparse MoE layers, where each token of image patch is routed to a subset of experts, i.e., MLP layers.
The DiT-MoE includes two simple designs: shared expert routing and expert-level balance loss, thereby capturing common knowledge and reducing redundancy among the different routed experts. When applied to conditional image generation, a deep analysis of experts specialization gains some interesting observations: (i) Expert selection shows preference with spatial position and denoising time step, while insensitive with different class-conditional information; (ii) As the MoE layers go deeper, the selection of experts gradually shifts from specific spatial position to dispersion and balance. (iii) Expert specialization tends to be more concentrated at the early time step and then gradually uniform after half.
Experiment results indicate that DiT-MoE matches the performance of state-of-the-art dense models, while requiring less time to inference. Alternatively, DiT-MoE-S can match the cost of DiT-B while achieving better performance. Further, DiT-MoE with synthesized image data, were able to scale at a 16.5B parameter, while only activating 3.1B parameters, attaining a new SoTA FID-50K score of 1.80 in 512×512 resolution settings.
Paper : https://arxiv.org/pdf/2407.11633