Recent progress in instruction tuned LLM highlights the critical role of high-quality data in enhancing LLMs’ instruction-following capabilities. However, acquiring such data through human annotation remains cost-prohibitive and difficult to scale, hindering further progress. Using LLMs generated instruction aligned synthetic data have often shown to neglect downstream use cases.
So how can we tailor synthetic data to align LLMs for different instruction-following tasks?
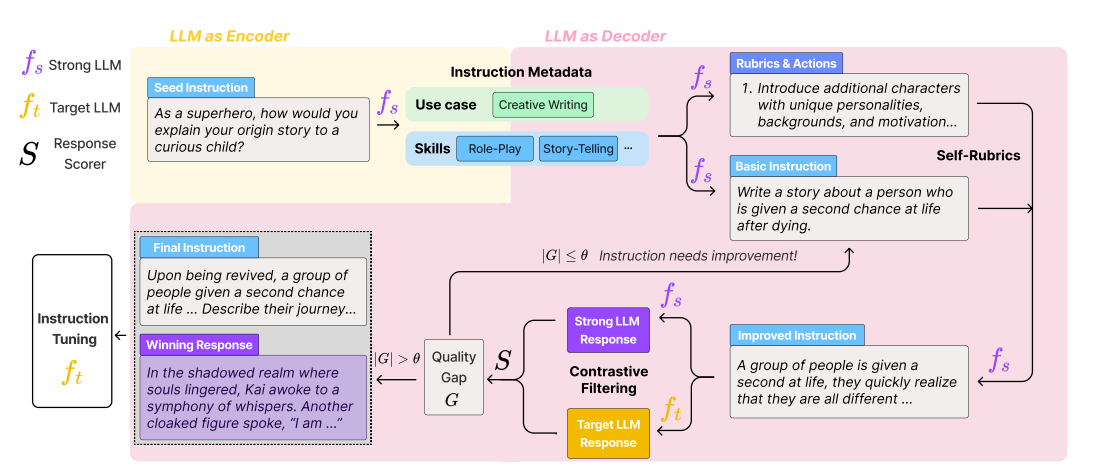
To address this researchers have introduced CodecLM, a general framework for adaptively generating high quality synthetic data for LLM alignment with different downstream instruction distributions and LLMs. Drawing on the Encode-Decode principles CodecLM works as follows: First, the strong LLM (fs) encodes the seed instruction into instruction metadata, specifying its use case and skills required for responses. Next, fs decodes metadata into basic instructions. Meanwhile, Self-Rubrics leverages fs to generate rubrics and actions to improve the basic instruction, tailoring them for the downstream task. Finally, Contrastive Filtering uses a scoring function S to compare fs and ft’s responses. The most effective pairs are selected for aligning the LLM, while less effective instructions are sent for further improvement.
CodecLM was evaluated on various benchmarks including EvolInstruct, Vicuna, Self-Instruct and Koala and against various methods Self-Instruct, Alpagasus, Tree-Instruct, WizardLM and WizardLM+. All methods were trained on LLaMA-7B or 13B as the target LLM and compared against Gemini-Pro, the strong LLM that generates the data. CodecLM outperforms against all methods consistently on all benchmarks, with both the target LLMs.