Vision language models (VLMs) like GPT-4, LLaMAadapter, and LLaVA have been instrumental in augmenting LLMs with visual understanding capabilities. VLMs serve as foundational models in tackling a wide array of tasks including Visual Question Answering (VQA), captioning, and visual content generation. However, there has not been much progress to improve VLMs performance mainly due to LLMs transformer architecture, which has a less efficient quadratic computation complexity.
So can VLMs based on non transformer architecture like Mamba perform better than transformer one ?
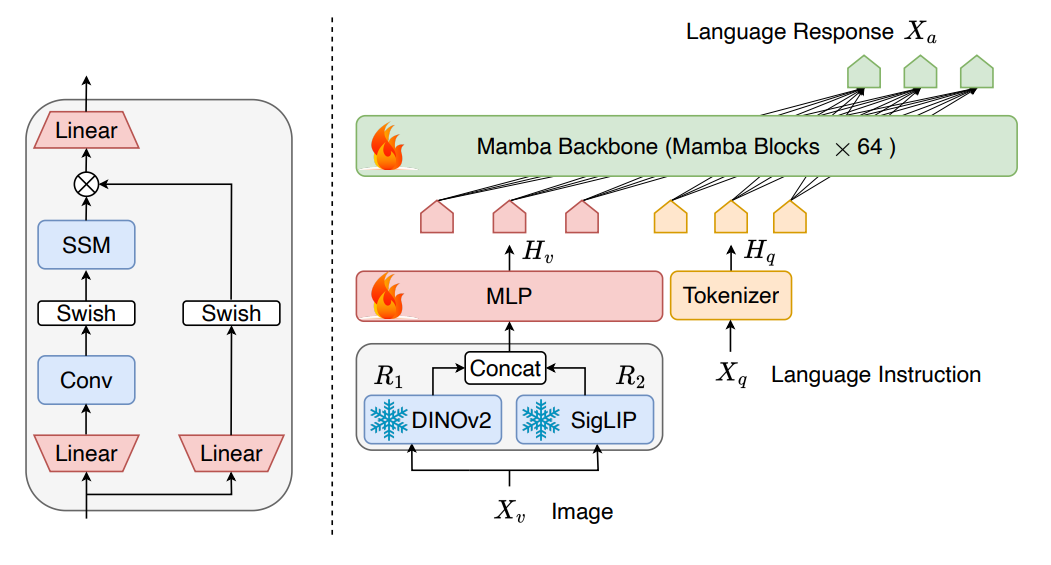
Well that’s what researchers from Westlake University have addressed with Cobar, an efficient Mamba language model with integrated visual modality. Cobar consists of three components: a vision encoder, a projector, and a Mamba backbone. For vision encoder DINOv2 and SigLIP are fused and used as vision backbone. The intuition is that combining the visual representations, which capture low-level spatial properties from DINOv2 and the semantic properties provided by SigLIP further improves the performance on downstream tasks. The projector is a simple learnable MLP that aligns the features of vision and text. Finally, the LLM backbone is a Mamba language model with 2.8B parameters. During training, the parameters of vision encoders are frozen and the parameters of the projector and Mamba LLM backbone are fine-tuned.
During experimentation several ablation studies on projectors (MLP or Lightweight Downsample Projector), vision backbones (DINOv2 + SigLIP or SigLIP only), and LLM backbones (base model or instruction-tuned chat model) was carried out. Compared with Baselines, Cobra achieves comparable performance to LLaVA v1.5 7B with about 43% of the number of parameters. Inference Speed, Cobra performs 3× ∼ 4× faster than MobileVLM v2 3B and TinyLLaVA 3B on a single NVIDIA A100 80G GPU. Overall, Cobra is competitive in the field of Visual Large Language Models (VLLM), especially in processing visual information and generating natural language descriptions.