Self-attention, one of the critical components in LLM, has a poor performance during inference since it performs intensive memory operations on key/value tensors of context tokens (KV cache) and is memory-bound. Due to which it becomes a significant source of inference latency for long sequences. To negate this it’s now common to use prompt prefixes caching during multi-tenant LLMs serving scenarios. But there are some limitations to this (1) predefined system prompts are static and inflexible in frequent refreshes for large scale deployments (2) there is memory waste in case of long system prompts and low hit rate.
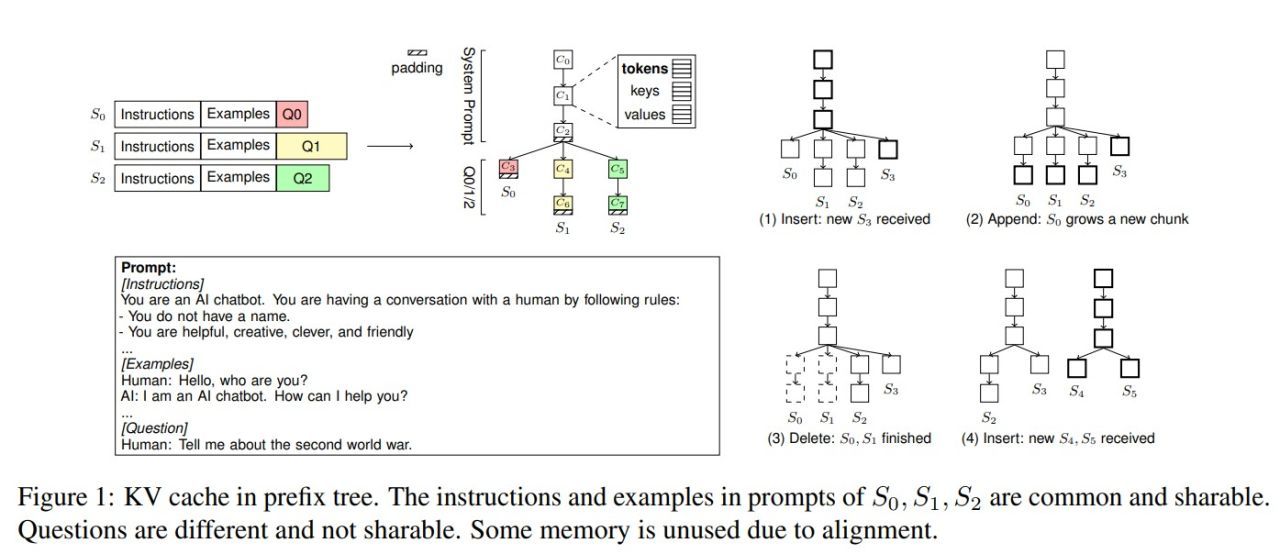
To address this paper has introduced ChunkAttention, a prefix aware self-attention module that can detect matching prompt prefixes across multiple requests and share their key/value tensors in memory at runtime to improve the memory utilization of KV cache. This is achieved by breaking monolithic key/value tensors into smaller chunks and structuring them into the auxiliary prefix tree. Consequently, on top of the prefix-tree based KV cache, an efficient self-attention kernel, where a two-phase partition algorithm is implemented to improve the data locality during self-attention computation in the presence of shared system prompts.
Experiments show that ChunkLlama (ChunkAttention on Llama) can achieve comparable throughput with SOTA PagedAttention kernel without shared system prompts and can outperform it by 3.2-4.8× with a shared system prompt of 1024 to 4096 tokens on A100 (80G) by applying prefix-aware KV cache and two-phase partition. ChunkLlama can achieve 1.6× (2.9 against 1.8) and 2.3× (2.3 against 1.0) higher throughput compared to vLLM when 1024 and 2048 prefix tokens are shared while maintaining a normalized latency of less than 40 ms/token. The KV cache memory usage is reduced by 70%-90% with long shared prefixes. The peak batch size is also reduced by 20%-40% since ChunkLlama can decode faster.