With all open source LLM models trying to outperform GPT-4 one may wonder, which one has truly been successful in Conversational QA - one of the elementary use cases of LLMs.
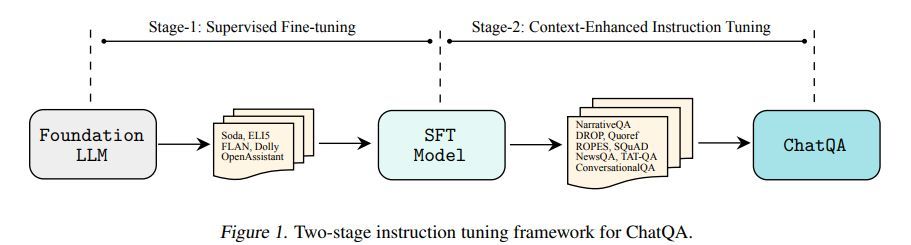
Introducing ChatQA, a family of conversational question answering (QA) models, that obtain GPT-4 level accuracies. It proposes a two-stage instruction tuning method that can significantly improve the zero-shot conversational QA results from large language models (LLMs). To handle retrieval in conversational QA, it fine-tunes a dense retriever on a multiturn QA dataset, which provides comparable results to using the state-of-the-art query rewriting model while largely reducing deployment cost. Notably, ChatQA-70B can outperform GPT-4 in terms of average score on 10 conversational QA datasets (54.14 vs. 53.90), without relying on any synthetic data from OpenAI GPT models
In addition, it demonstrates that fine-tuning a single-turn query retriever using its own curated conversational QA data performs comparable to the state-of-the-art LLM-based query rewriting model, without the need of extra computational time and potential API cost from rewriting.
Paper : https://arxiv.org/pdf/2401.10225.pdf
arxiv:2401.10225