Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) has emerged as a prominent framework for building ML/AI solutions with LLMs. Additional modules such as query rewriting, prompt compression, and query routing have been integrated with RAG to enhance its performance. However, such integration has led to additional complexity namely hyper-parameters within the modules and incorporating human-in loop feedback in the modules.
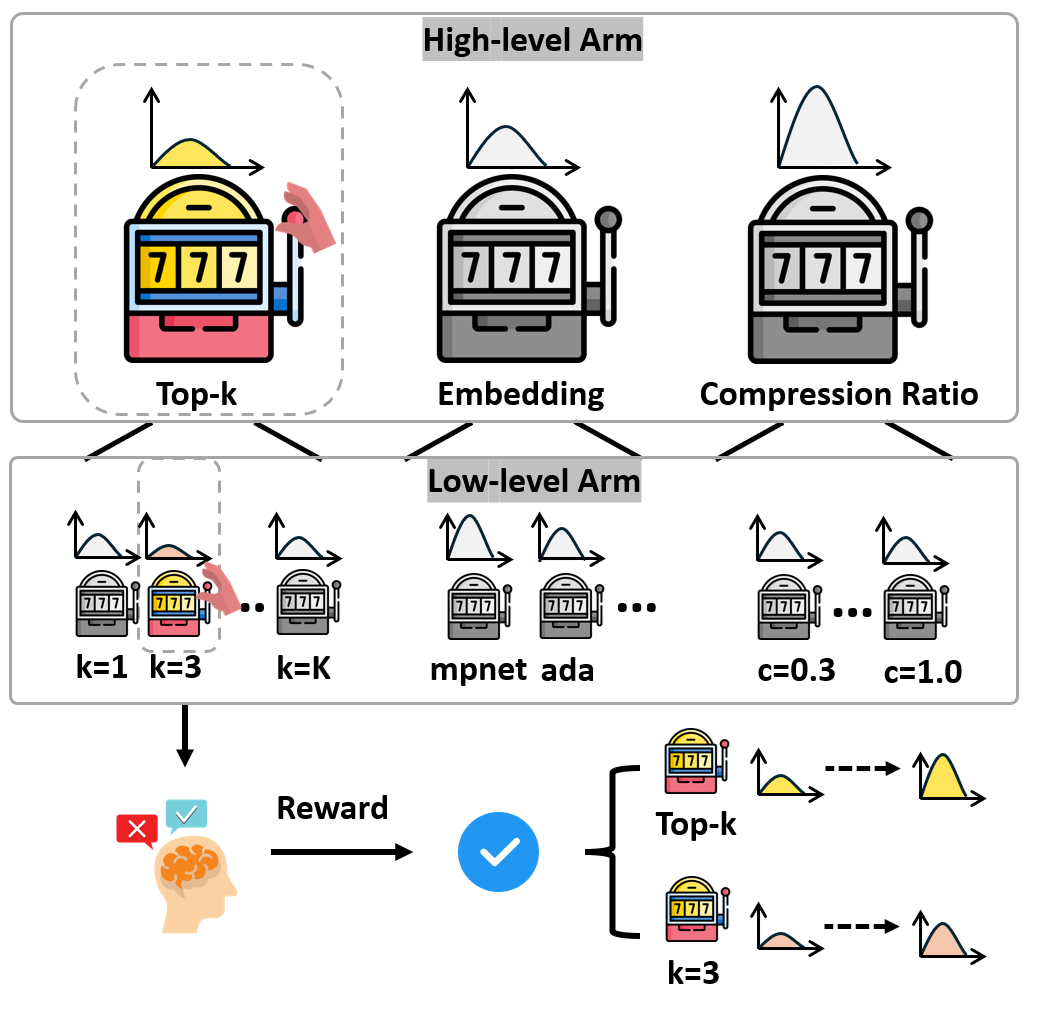
To address such challenges researchers have proposed the AutoRAGHP framework, which formulates the hyperparameter tuning as an online multi-armed bandit (MAB) problem and introduces a novel two level Hierarchical MAB (Hier-MAB) method for efficient exploration of large search spaces.
AutoRAG-HP uses two-level Hier-MAB in the context of jointly tuning of top-k (K), embedding model (E), and compression ratio (C) hyper-parameters. The high-level arm is responsible for selecting which hyper-parameter to tune, while the lower-level arms control the hyperparameter selection within the search space of each hyper-parameter.
After pulling the two-level arms and observing the associated reward, the algorithm updates its estimate of the selected arm’s reward distribution using the new information, i.e., updating the mean reward estimation and the confidence interval based on the observed reward. Meanwhile, the reward distributions of other high- and low-level arms pulled in previous iterations also get updated. This process repeats for a predetermined number of iterations or until a stopping criterion is met.
AutoRAG-HP was evaluated on tuning hyper-parameters, such as top-k retrieved documents, prompt compression ratio, and embedding methods, using the ALCE-ASQA and Natural Questions datasets. AutoRAG-HP demonstrates that MAB-based online learning methods can achieve Recall@5 ≈ 0.8 for scenarios with prominent gradients in search space, using only ∼ 20% of the LLM API calls required by the Grid Search approach.
Paper : https://arxiv.org/pdf/2406.19251