Synthetic data is becoming increasingly important for accelerating the development of language models, both large and small. Despite several successful use cases, researchers also raised concerns around model collapse and drawbacks of imitating other models. Effective use of synthetic data usually requires significant human effort in curating the data and mostly uses prompts and a powerful model such as GPT-4 or Llama to generate such post-training synthetic data.
To address these issues researchers have introduced AgentInstruct, an extensible agentic framework for automatically creating large amounts of diverse and high-quality synthetic data that surpasses underlying LLMs. The AgentInstruct comprises four primary stages:
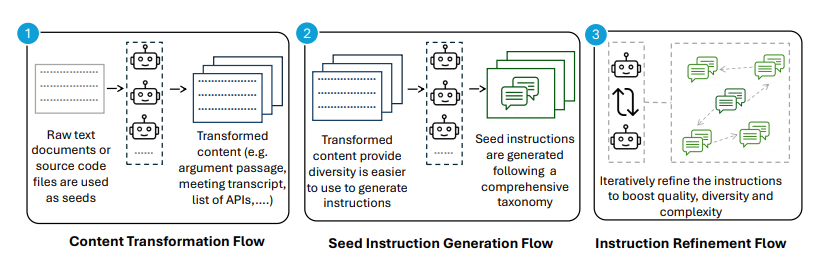
Seed Collection: This step involves gathering a varied set of initial sources such as textbook sections, web articles, and code snippets. These sources serve as the foundational material for creating new instructions.
Content Transformation: Specialized agents process each seed into an intermediate form that facilitates the creation of instructions. These agents are capable of tasks like generating argument passages, debates, conversations, meeting transcripts, poems, and satirical content, among others.
Seed Instruction Generation: In this phase, multiple agents take the transformed seed and generate a wide range of instructions using a predefined taxonomy of instruction types. For instance, in the field of reading comprehension, this taxonomy includes 43 types of questions, covering literal comprehension, critical analysis, and inference.
Instruction Refinement: The final stage focuses on improving the complexity and quality of the generated instructions through an iterative process. Suggester-editor agent pairs work together: suggest agents propose ways to increase the complexity of instructions, while editor agents make corresponding modifications to enhance their quality.
Using AgentInstruct researchers were able to generate around 22 million instructions. These were integrated with 3.8 million instructions sourced elsewhere, resulting in a dataset totaling 25.8 million paired instructions. This extensive dataset was then employed to fine-tune the Mistral-7b model, leading to the development of the Orca-3 model.
Paper : https://arxiv.org/pdf/2407.03502